Brother International HL-5255DN-MICR MICR Network Owner's Manual - English - Page 14
Configuring your network printer, Overview, IP addresses, subnet masks and gateways
 |
View all Brother International HL-5255DN-MICR manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
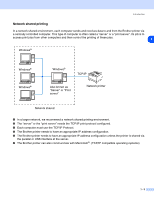
2 Configuring your network printer Overview Before using your Brother printer in a network environment, you must configure the TCP/IP settings. In this 2 chapter, you will learn the basic steps required to print over the network using the TCP/IP protocol. Note You can configure the printer's TCP/IP settings using the control panel on the printer (for HL-5270DN). For further information, see Control panel setup in Chapter 7. We recommend that you use the automatic installer application in the CD-ROM we have provided with the printer. By using this application, you can easily connect your printer to your network and install the network software and printer driver which you need to complete the network configuration. You will be guided by the on-screen instructions until you are able to use your Brother network printer. Please follow the instructions in the supplied Quick Setup Guide. If you want to configure your printer without using the automatic installer application, please read this chapter and learn how to configure the TCP/IP settings. Then, in Chapter 3, Chapter 4, Chapter 5 and Chapter 6, you will learn how to install the network software and the printer driver into the operating system running on your computer. IP addresses, subnet masks and gateways To use the printer in a networked TCP/IP environment, you need to configure the IP address and subnet mask. The IP address you assign to the print server must be on the same logical network as your host computers. If it is not, you must properly configure the subnet mask and the gateway address. IP address An IP address is a series of numbers that identifies each computer connected to a network. An IP address consists of four numbers separated by dots. Each number is between 0 and 255. Example: In a small network, set the IP addresses by changing the final number. 192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2, 192.168.1.3 2 - 1