Campbell Scientific CS616 CS616 and CS625 Water Content Reflectometers - Page 10
Installation
 |
View all Campbell Scientific CS616 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
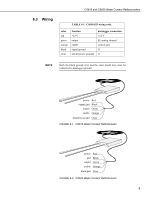
CS616 and CS625 Water Content Reflectometers 5.4 Operational Details The accuracy specification for the volumetric water content measurement using the CS616/CS625 probes is based on laboratory measurements in a variety of soils and over the water content range air dry to saturated. The soils were typically sandy loam and coarser. Silt and clay were present in some of the soils used to characterize accuracy. Resolution is the minimum change in the dielectric permittivity that can reliably be detected by the water content reflectometer. The CS616 or CS625 is typically used to measure soil volumetric water content. Precision describes the repeatability of a measurement. It is determined for the CS616 and CS625 by taking repeated measurements in the same material. The precision of the CS616/CS625 is better than 0.1 % volumetric water content. Soil Properties The water content reflectometer operation can be affected when the signal applied to the probe rods is attenuated. The probe will provide a well-behaved response to changing water content, even in attenuating soils or other media, but the response may be different than described by the standard calibration. Consequently, a unique calibration is required. Change in probe response can occur when soil bulk electrical conductivity is greater than 0.5 dS m-1. The major contributor to soil electrical conductivity is the presence of free ions in solution from dissolution of soil salts. Soil organic matter and some clays can also attenuate the signal. 6. Installation 6.1 Orientation The probe rods can be inserted vertically into the soil surface or buried at any orientation to the surface. A probe inserted vertically into a soil surface will give an indication of the water content in the upper 30 cm of soil. The probe can be installed horizontal to the surface to detect the passing of wetting fronts or other vertical water fluxes. A probe installed at an angle of 30 degrees with the surface will give an indication of the water content of the upper 15 cm of soil. 6.2 Potential Problems with Improper Insertion The method used for probe installation can affect the accuracy of the measurement. The probe rods should be kept as close to parallel as possible when installed to maintain the design wave guide geometry. The sensitivity of this measurement is greater in the regions closest to the rod surface than at distances away from the surface. Probes inserted in a manner which generates air voids around the rods will reduce the measurement accuracy. In most soils, the soil structure will recover from the disturbance during probe insertion. In some applications, installation can be improved by using the CS650G insertion guide tool. The CS650G is inserted into the soil and then removed. This makes proper installation of the water content reflectometer easier in dense or rocky soils. 4