Compaq R6000 Technology for remote management of power distribution - Page 2
Abstract, Introduction
 |
UPC - 743172638854
View all Compaq R6000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 2 highlights
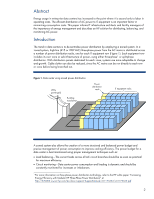
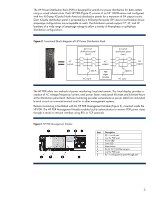
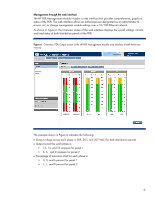
Abstract Energy usage in enterprise data centers has increased to the point where it is second only to labor in operating costs. The efficient distribution of AC power to IT equipment is an important factor in minimizing consumption costs. This paper informs IT infrastructure architects and facility managers of the importance of energy management and describes an HP solution for distributing, balancing, and monitoring AC power. Introduction The trend in data centers is to de-centralize power distribution by employing a zoned system. In a zoned system, high-line (415 or 208 VAC) three-phase power from the AC mains is distributed across a number of power distribution racks, one for each IT equipment row (Figure 1). Each equipment row includes its own zone or sub-infrastructure of power, using either three-phase1 or split-phase distribution. With distribution panels dedicated for each zone, systems are more adaptable to change and growth. Cable clutter can also be reduced, since the AC mains can be run directly to each row or zone before being branched out. Figure 1. Data center using zoned power distribution Utility power grid Building transformer Power distribution rack IT equipment racks A zoned system also allows the creation of a more structured and balanced power budget and precise management of power consumption to improve cooling efficiency. The power budget for a date center is best maintained using proper management techniques such as: • Load balancing-The current loads across all AC circuit branches should be as even as practical for maximum efficiency. • Circuit monitoring-Data center power consumption and loading is dynamic and should be constantly monitored for increases or imbalances. 1 For more information on three-phase power distribution technology, refer to the HP white paper "Increasing Energy Efficiency with Modular HP Three-Phase Power Distribution" at http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c01173322/c01173322.pdf 2