D-Link DGS-1016TG User Guide - Page 9
Switch Description, Features
 |
UPC - 790069262142
View all D-Link DGS-1016TG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
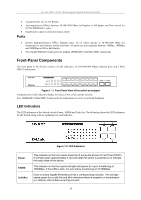
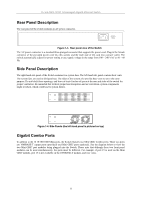
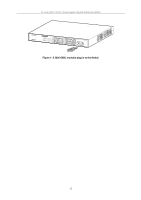
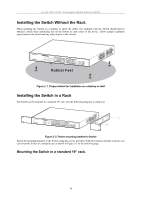
D-Link DGS-1016T Unmanaged Gigabit Ethernet Switch network to be divided into different segments which don't compete with each other for network transmission capacity, giving a decreased load on each. The switch acts as a high-speed selective bridge between the individual segments. Traffic that needs to go from one segment to another (from one port to another) is automatically forwarded by the switch, without interfering with any other segments (ports). This allows the total network capacity to be multiplied, while still maintaining the same network cabling and adapter cards. For Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet networks, a switch is an effective way of eliminating problems of chaining hubs beyond the "two-repeater limit." A switch can be used to split parts of the network into different collision domains, for example, making it possible to expand your Fast Ethernet network beyond the 205-meter network diameter limit for 100BASE-TX networks. Switches supporting both traditional 10Mbps Ethernet and 100Mbps Fast Ethernet are also ideal for bridging between existing 10Mbps networks and new 100Mbps networks. Switching LAN technology is a marked improvement over the previous generation of network bridges, which were characterized by higher latencies. Routers have also been used to segment local area networks, but the cost of a router and the setup and maintenance required make routers relatively impractical. Today's switches are an ideal solution to most kinds of local area network congestion problems. Switch Description The DGS-1016T Switch module is equipped with sixteen ports providing dedicated 10, 100 or 1000 Mbps bandwidth. These ports can be used for connecting PCs, servers, and hubs. The sixteen dual speed ports use standard twisted pair cabling and are ideal for segmenting networks into small, connected subnets. Each port can support up to 2000 Mbps of throughput in full-duplex mode. In addition, the Switch is equipped with two Mini GBIC uplink ports enabling convenient access to a server or network backbone for all the clients served by the Switch. This stand-alone Switch enables the network to use some of the most demanding multimedia and imaging applications concurrently with other user applications without creating bottlenecks. Features • Sixteen 1000BASE-T Gigabit ports for connections to server or network backbone • IEEE 802.3 compliant • IEEE 802.3ab compliant • IEEE 802.3u compliant • IEEE 802.3z compliant • IEEE 802.3x flow control for full duplex mode • Full and half-duplex for both 10Mbps and 100Mbps connections. The 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet module operates at full-duplex only. Full-duplex allows the switch port to simultaneously transmit and receive data, and only works with connections to full-duplex capable end stations and switches. Connections to a hub must take place at half-duplex • Store and forward switching scheme capability to support rate adaptation and protocol conversion • Data forwarding rate 14,880 pps per port at 100% of wire-speed for 10Mbps speed • Data forwarding rate 148,810 pps per port at 100% of wire-speed for 100Mbpsspeed • Data forwarding rate 1,488,100 pps per port at 100% of wire-speed for 1000Mbps speed • Data filtering rate eliminates all error packets, runts, etc. at 14,880 pps per port at 100% of wire-speed for 10Mbps speed • Data filtering rate eliminates all error packets, runts, etc. at 148,810 pps per portat 100% of wire-speed for 100Mbps speed • Data filtering rate eliminates all error packets, runts, etc. at 1,488,100 pps per port at 100% of wirespeed for 1000Mbps speed • Layer 2 switching based on MAC address • Address handling: auto-learning, auto-aging • MAC Address table: Support addresses up to 4K 9