Edimax BR-6478AC User Manual - Page 140
Access point, Subnet Mask, TCP/IP, UDP, based management Graphical User Interface GUI
 |
View all Edimax BR-6478AC manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 140 highlights
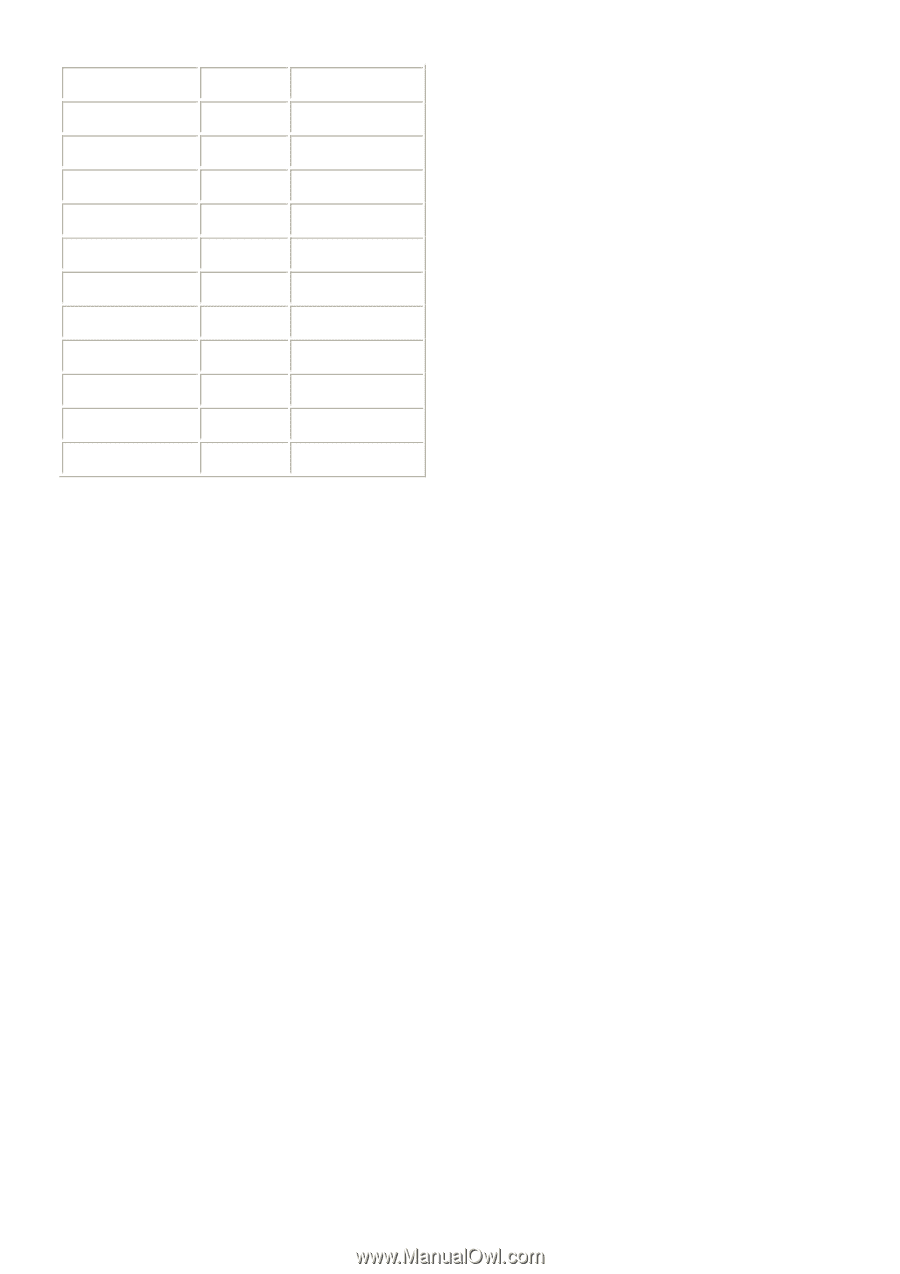
Application Protocol Port Number Telnet TCP 23 FTP TCP 21 SMTP TCP 25 POP3 TCP 110 H.323 TCP 1720 SNMP UCP 161 SNMP Trap UDP 162 HTTP TCP 80 PPTP TCP 1723 PC Anywhere TCP 5631 PC Anywhere UDP 5632 Access point: A access point is an intelligent network device that forwards packets between different networks based on network layer address information such as IP addresses. Subnet Mask: A subnet mask, which may be a part of the TCP/IP information provided by your ISP, is a set of four numbers (e.g. 255.255.255.0) configured like an IP address. It is used to create IP address numbers used only within a particular network (as opposed to valid IP address numbers recognized by the Internet, which must be assigned by InterNIC). TCP/IP, UDP: Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and Unreliable Datagram Protocol (UDP). TCP/IP is the standard protocol for data transmission over the Internet. Both TCP and UDP are transport layer protocol. TCP performs proper error detection and error recovery, and thus is reliable. UDP on the other hand is not reliable. They both run on top of the IP (Internet Protocol), a network layer protocol. WAN: Wide Area Network. A network that connects computers located in geographically separate areas (e.g. different buildings, cities, countries). The Internet is a wide area network. Web‐based management Graphical User Interface (GUI): Many devices support a graphical user interface that is based on the web browser. This means the user can use the familiar Netscape or Microsoft Internet Explorer to Control/configure or monitor the device being managed. 136