Edimax ES-5808PHG Manual - Page 30
RSTP Port Status
 |
View all Edimax ES-5808PHG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
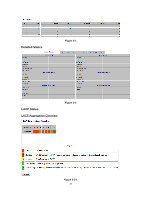
¾Fwd Delay: The maximum time (in seconds) the root device will wait before changing states (i.e., discarding to learning to forwarding). This delay is required because every device must receive information about topology changes before it starts to forward frames. In addition, each port needs time to listen for conflicting information that would make it return to a discarding state; otherwise, temporary data loops might result. ¾Topology: Indicates if spanning tree topology is steady or undergoing reconfiguration. (The time required for reconfiguration is extremely short, so no values other that "steady" state are likely to be seen in this field.) ¾Root ID : The priority and MAC address of the device in the Spanning Tree that this switch has accepted as the root device, and the port connected to the root device. RSTP Port Status Figure 2-4-2 ¾ Port/Group: The number of a port or the ID of a static trunk. ¾ Path Cost: The cost for a packet to travel from this port to the root in the current Spanning Tree configuration. The slower the media, the higher the cost. ¾ Edge Port: Shows if this port is functioning as an edge port, either through ¾ manual selection (see the RSTP Port Configuration table) or auto-detection. Note that if the switch detects another bridge connected to this port, the manual setting for Edge Port will be overridden, and the port will instead function as a point-to-point connection. ¾ P2P Port: Shows if this port is functioning as a Point-to-Point connection to exactly one other bridge. The switch can automatically determine if the interface is attached to a point-to-point link or to shared media. If shared media is detected, the switch will assume that it is connected to two or more bridges. 29