Gigabyte GV-R13128D Manual - Page 28
GV-R13128D Graphics Accelerator
 |
View all Gigabyte GV-R13128D manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 28 highlights
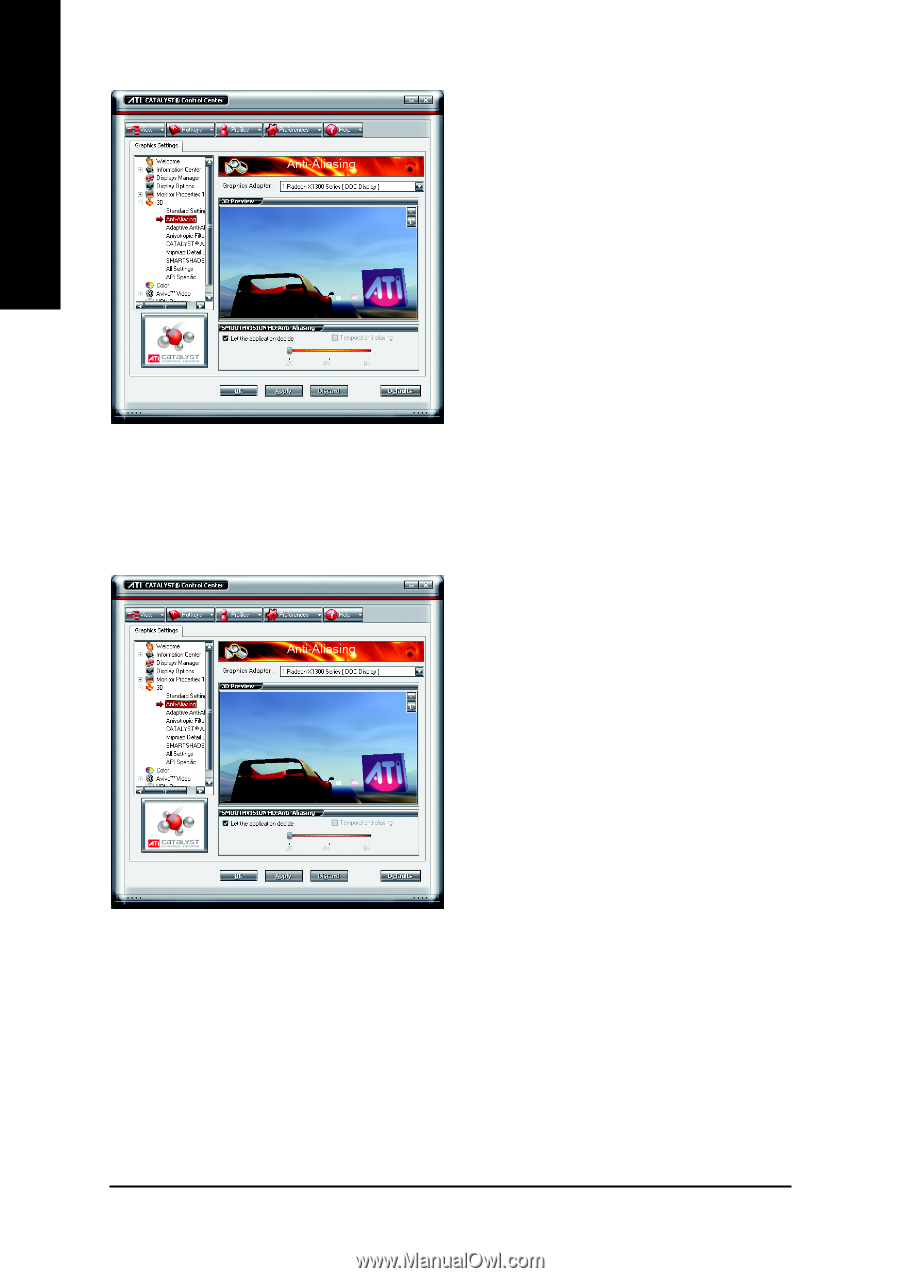
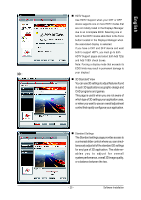
English Anti-Aliasing Anti-Aliasing is a technique used to smooth out the jagged edges of three-dimensional curved objects or objects with diagonal edges. Anti-aliasing can be set to favor either an increase in system processing performance or improved image quality: Setting for performance is best used when the 3D image is animated and smoothness of motion is the most important consideration. Setting for quality is best used when having highly detailed and realistic 3D objects is the primary concern. If you are unsure of how to configure anti-aliasing, use the Let the Application Decide option. Your display will automatically adjust to the application's requirements. Adaptive Anti-Aliasing Adaptive anti-aliasing is a technique that applies a combination of multi-sampling (MSAA) and super-sampling (SSAA) on 3D objects to improve edge smoothness and fine detail. Multisampling works best on smoothing the edges of solid polygons, but cannot effectively smooth edges within polygons which are partially transparent. Super-sampling is able to more accurately calculate color values adjacent to transparent pixel shader values within polygons with partially transparent textures, but is not applied universally since it is more processor-intensive. Adaptive anti-aliasing works by using super-sampled anti-aliasing on transparent textures, and multi-sampled anti-aliasing on all other textures. This delivers exceptional levels of image quality, while maintaining performance. GV-R13128D Graphics Accelerator - 26 -