HP 40g hp 39g & 40g_user's manual_English_E_pdfbpia5212.pdf - Page 193
MATH menu. Press
 |
View all HP 40g manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 193 highlights
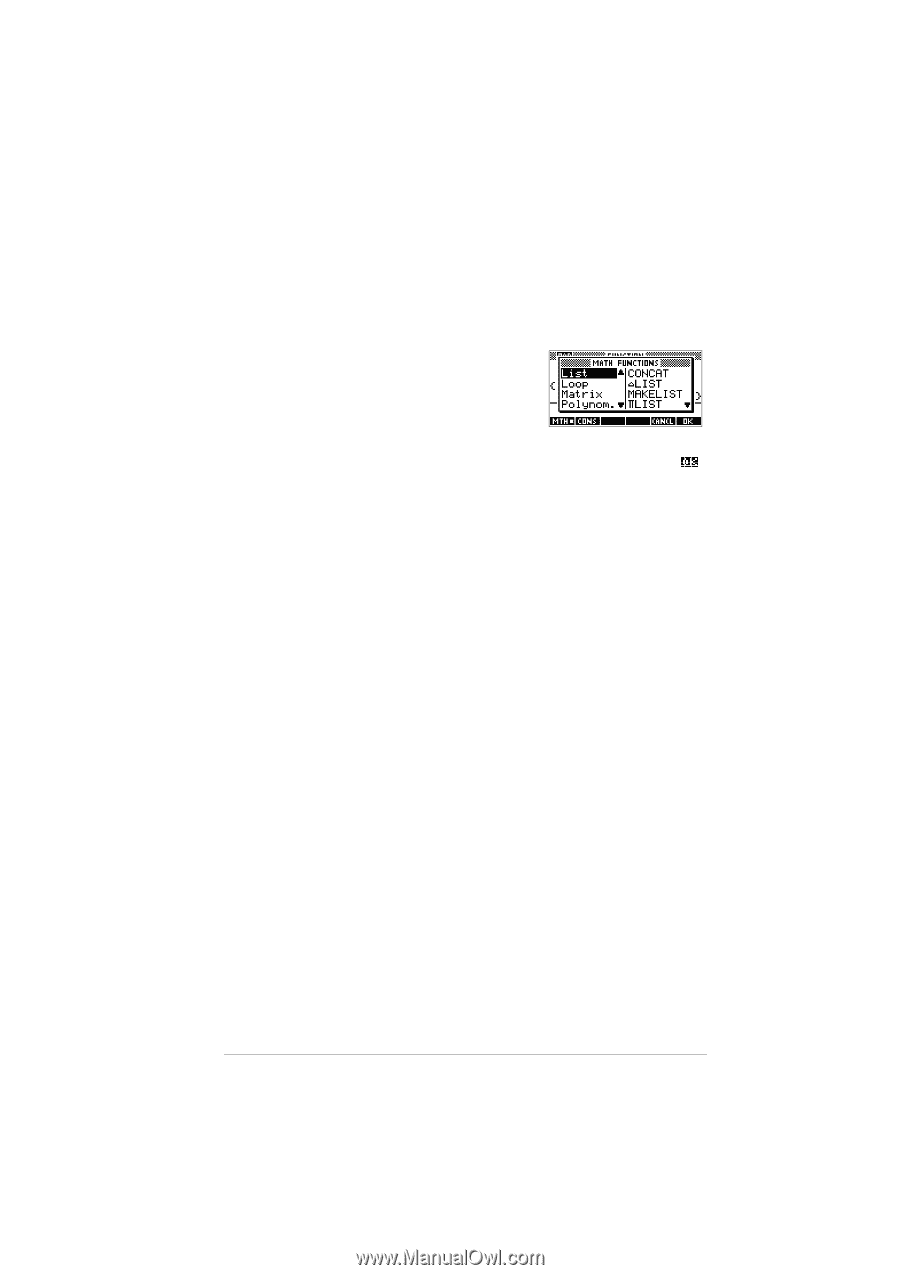
List functions Following are details of list functions. You can use them in HOME, as well as in programs. You can type in the name of the function, or you can copy the name of the function from the List category of the MATH menu. Press (the alpha L character key). This displays the List category. Press , select a function, and press . List functions have the following syntax: • Functions have arguments that are enclosed in parentheses and separated by commas. Example: CONCAT(L1,L2). An argument can be either a list variable name (such as L1) or the actual list. For example, REVERSE({1,2,3}). • If Decimal Mark in MODES is set to Comma, use periods to separate arguments. For example, CONCAT(L1.L2). Common operators like +, -, ×, and / can take lists as arguments. If there are two arguments and both are lists, then the lists must have the same length, since the calculation pairs up the elements. If there are two arguments and one is a real number, then the calculation pairs the number with each element of the list. Example 5*{1,2,3} returns {5,10,15}. Besides the common operators that can take numbers, matrices, or lists as arguments, there are commands that can only operate on lists. Lists 13-7