HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch TRILL Configuration Guide - Page 4
Configuring TRILL, Overview, Basic concepts, TRILL frame formats
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 4 highlights
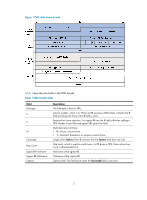
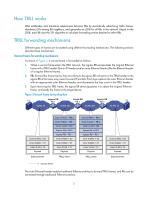
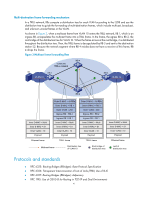
Configuring TRILL Transparent Interconnect of Lots of Links (TRILL) uses IS-IS to provide transparent Layer 2 forwarding. Overview TRILL combines the simplicity and flexibility of Layer 2 switching with the stability, scalability, and rapid convergence capability of Layer 3 routing. All these advantages make TRILL very suitable for large flat Layer 2 networks in data centers. Basic concepts • RBridge-Routing bridge (RB for short) that runs TRILL. RBs are classified into ingress RBs, transit RBs, and egress RBs, depending on their positions in the TRILL network. A frame enters the TRILL network through an ingress RB, travels along transit RBs, and leaves the TRILL network through an egress RB, as shown in Figure 2. • TRILL network-A Layer 2 network comprised of RBs, as shown in Figure 3. • Nickname-Unique identifier of an RB in the TRILL network. TRILL automatically assigns nicknames to RBs. • Link State Database-The LSDB contains all link state information in the TRILL network. • Link State Protocol Data Unit-An LSP describes local link state information and is advertised between neighbor devices. • Appointed VLAN-x Forwarder (AVF) and appointed port-TRILL supports VLANs. To avoid loops, TRILL requires all the traffic of a VLAN on a network segment to enter and leave the TRILL network through the same port of an RB. The RB is the AVF of the VLAN, and the port is the appointed port. • Designated Routing Bridge-The DRB corresponds to the DIS in IS-IS. It helps simplify network topology and appoints AVFs for VLANs on each RB. For more information about LSDB, LSPDU, and DIS, see Layer 3-IP Routing Configuration Guide. TRILL frame formats TRILL frames include control frames and data frames. TRILL control frames include TRILL Hello, LSP, CSNP, PSNP, MTU-prob, and MTU-ack. These control frames use 802.1Q encapsulation, and have a fixed destination multicast address 0180-C200-0041. TRILL data frames have a specific format, as shown in Figure 1. A TRILL header and an outer Ethernet header are added to the original Ethernet frame. 1