HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch TRILL Configuration Guide - Page 6
How TRILL works, TRILL forwarding mechanisms, Unicast frame forwarding mechanism
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
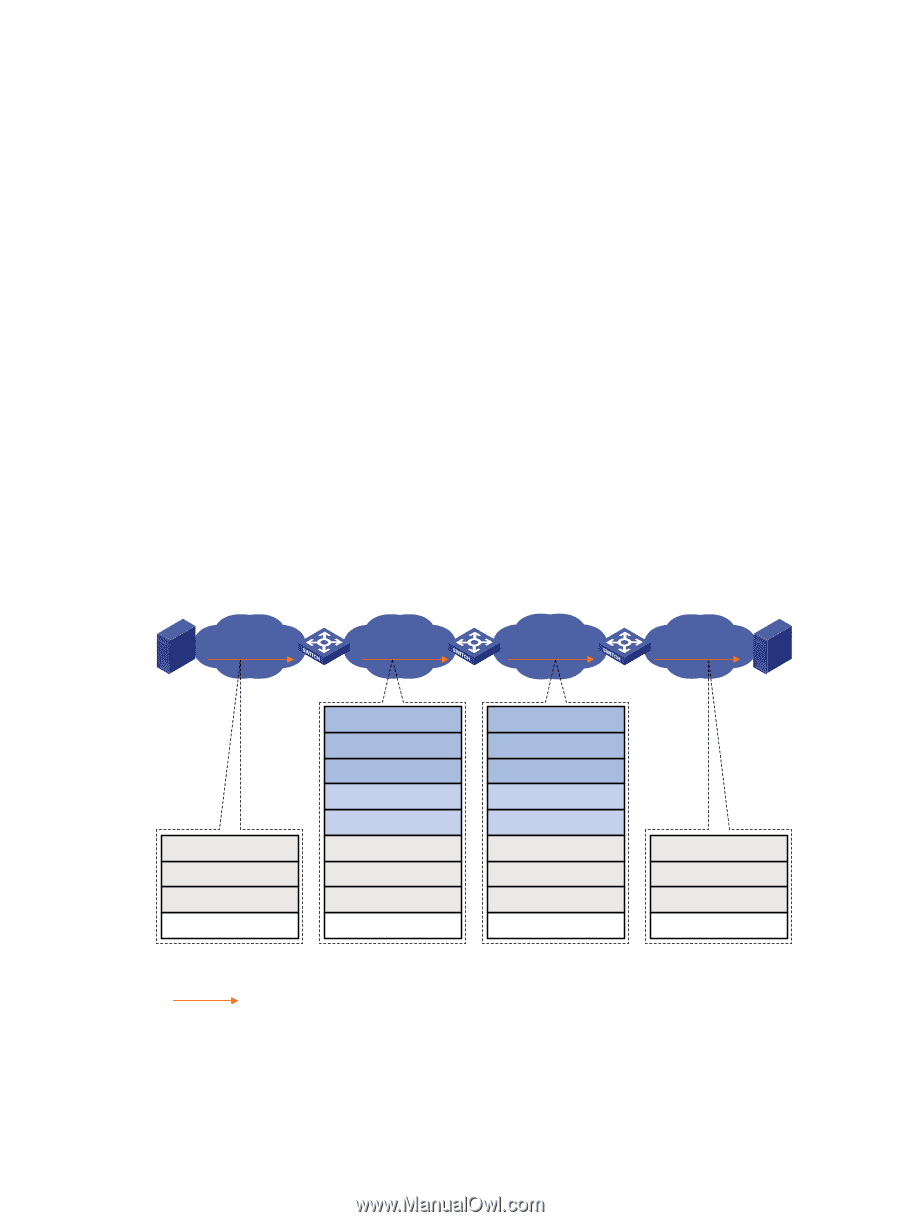
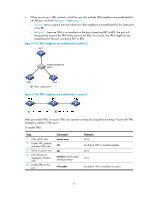
How TRILL works TRILL establishes and maintains adjacencies between RBs by periodically advertising Hello frames, distributes LSPs among RB neighbors, and generates an LSDB for all RBs in the network. Based on the LSDB, each RB uses the SPF algorithm to calculate forwarding entries destined to other RBs. TRILL forwarding mechanisms Different types of frames are forwarded using different forwarding mechanisms. The following sections describe these mechanisms. Unicast frame forwarding mechanism As shown in Figure 2, a unicast frame is forwarded as follows: 1. When a unicast frame enters the TRILL network, the ingress RB encapsulates the original Ethernet frame with a TRILL header (like an IP header) and an outer Ethernet header (like the Ethernet header of a regular Ethernet frame). 2. RBs forward the frame hop by hop according to the egress RB nickname in the TRILL header to the egress RB in the same way routers forward IP packets. Each hop replaces the outer Ethernet header with an appropriate outer Ethernet header, and decrements the hop count in the TRILL header. 3. Upon receiving the TRILL frame, the egress RB de-encapsulates it to obtain the original Ethernet frame, and sends the frame to the target device. Figure 2 Unicast frame forwarding flow S1 Ingress RB RB 1 Transit RB RB 2 Egress RB RB 3 S2 VLAN 10 VLAN 200 VLAN 300 VLAN 10 Inner D-MAC = S2 Inner S-MAC = S1 Inner VLAN = 10 Payload Ethernet frame Outer D-MAC = RB 2 Outer S-MAC = RB 1 Outer VLAN = 200 Egress RB = RB 3 Ingress RB = RB 1 Inner D-MAC = S2 Inner S-MAC = S1 Inner VLAN = 10 Payload TRILL frame Unicast frame Outer D-MAC = RB 3 Outer S-MAC = RB 2 Outer VLAN = 300 Egress RB = RB 3 Ingress RB = RB 1 Inner D-MAC = S2 Inner S-MAC = S1 Inner VLAN = 10 Payload TRILL frame Inner D-MAC = S2 Inner S-MAC = S1 Inner VLAN = 10 Payload Ethernet frame The outer Ethernet header enables traditional Ethernet switches to forward TRILL frames, and RBs can be connected through traditional Ethernet switches. 3