HP 800 HP DLPI Programmer's Guide - Page 27
DA/SA MAC address, SAP/Ethertype, SNAP SAP = 0xAA, DA/SA, DSAP/SSAP, RIF, up to 18bytes]
 |
View all HP 800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 27 highlights
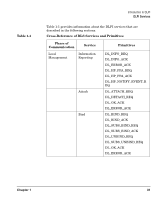
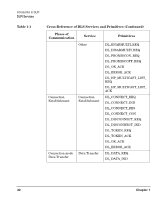
NOTE Chapter 1 Introduction to DLPI The Data Link Layer The basic DLSAP address format is as follows: | DA/SA MAC address | SAP/Ethertype | SNAP (SAP = 0xAA) | [RIF] | where, '[ ]' indicates that the information is optional. The three possible variations of the DLSAP address format based on the protocol value are as follows: • 802.2 SAP format | DA/SA | DSAP/SSAP | [RIF, up to 18bytes] | • Ethertype format | DA/SA | TYPE | • SNAP SAP format | DA/SA | 0xAA | SNAP | [RIF, up to 18bytes] | • HP Extended protocols (IEEESAP_HP/IEEESAP_NM) | DA/SA | DSAP/SSAP | DXSAP/SXSAP | where, '[ ]' indicates that the information is optional. For IP, the RIF information will be immediately following DA/SA and following that will be DSAP/SSAP. Certain DLS providers require the capability of binding on multiple DLSAP addresses. This can be achieved through subsequent binding of DLSAP addresses. DLPI supports peer and hierarchical binding of DLSAPs. When the user requests peer addressing, the DLSAP specified in a subsequent bind may be used in lieu of the DLSAP bound in the DL_BIND_REQ. This will allow for a choice to be made between a number of DLSAPs on a stream while determining traffic based on DLSAP values. 27