HP 800 HP DLPI Programmer's Guide - Page 40
Connection Handoff, accepted using DL_CONNECT_RES. DL_CONNECT_CON informs
 |
View all HP 800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 40 highlights
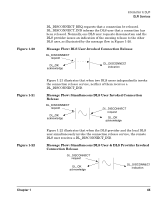
Introduction to DLPI DLPI Services Figure 1-12 Normal Connection Establishment In the connection establishment model, the caller initiates connection establishment, while the callee waits for incoming requests. DL_CONNECT_REQ requests that the DLS provider establish a connection. DL_CONNECT_IND informs the callee of the request, which may be accepted using DL_CONNECT_RES. DL_CONNECT_CON informs the caller that the connection has been established. The normal sequence of messages is illustrated in Figure 1-12. Message Flow: Successful Connection Establishment DL_CONNECT request DL_CONNECT indication DL_CONNECT confirm DL_CONNECT response DL_OK acknowledge Once the connection is established, the DLS users may exchange user data using DL_DATA_REQ and DL_DATA_IND. The DLS user may accept an incoming connect request on either the stream where the connect indication arrived or at an alternate, responding stream. The responding stream is indicated by a token in the DL_CONNECT_RES. This token is a value associated with the responding stream and is obtained by issuing a DL_TOKEN_REQ on that stream. The DLS provider responds to this request by generating a token for the stream and returning it to the DLS user in a DL_TOKEN_ACK. Connection Handoff Connections may be established on a stream other than that which received the DL_CONNECT_IND by passing a non-zero dl_resp_token in the DL_CONNECT_RES. The dl_resp_token value is obtained by doing a DL_TOKEN_REQ on the stream to which the connection is being passed (the data stream). The DL_CONNECT_RES is done on the stream which received the DL_CONNECT_IND (the control stream). Both the control and data streams must be bound on the same local SAP. After the DL_CONNECT_RES, the control stream will be left in the 40 Chapter 1