HP 800 HP DLPI Programmer's Guide - Page 36
Reserved IEEESAPS/Ethertypes, DL_BIND_REQ or the DL_SUBS_BIND_REQ DL_PEER_BIND class
 |
View all HP 800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 36 highlights
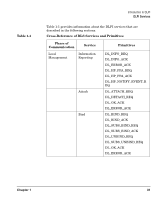
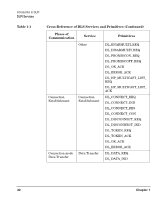
Introduction to DLPI DLPI Services • IEEE802.2 SAPS • ethernet types • SNAP Valid IEEE802.2 SAPS include even numbers from 0-255, excluding reserved SAPS (see "Reserved IEEESAPS/Ethertypes" on page 36). Valid ethernet types range from 0x600 to 0xFFFF, excluding reserved ethertypes (see "Reserved IEEESAPS/Ethertypes" on page 36). The SNAP protocol values contain three bytes of organization ID and two bytes of additional data. If the first three bytes are 0, the following two bytes are an ethernet type with valid values from 0x0-0xFFFF. If the first three bytes are non-zero, the following two bytes are organization specific with valid values from 0x0-0xFFFF. IEEE802.2 SAPS and ethernet types are bound to the driver via the DL_BIND_REQ or the DL_SUBS_BIND_REQ (DL_PEER_BIND class only). SNAP protocol values can be logged in two ways. The first method requires you to first bind the SNAP SAP 0xAA via the DL_BIND_REQ primitive. Then, you must issue a DL_SUBS_BIND_REQ (must be DL_HIERARCHICAL_BIND class) with five bytes of SNAP data. The second method requires you to bind any non-SNAP protocol value via the DL_BIND_REQ primitive, and then issue a DL_SUBS_BIND_REQ (must be DL_PEER_BIND class) with six bytes of data. The first byte must be the SNAP SAP 0xAA followed by five bytes of SNAP data. Reserved IEEESAPS/Ethertypes Refer to the IETF RFC 1010 (or superseding version) "Assigned Numbers". The DLS provider indicates success with a DL_BIND_ACK or a DL_SUBS_BIND_ACK message and failure with a DL_ERROR_ACK message. 36 Chapter 1