HP 9g hp 9g_user's manual_English_E_HDP1SG18ES1.pdf - Page 29
Relational Operators, Creating a New Program, Executing a Program - instructions
 |
View all HP 9g manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
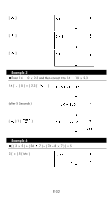
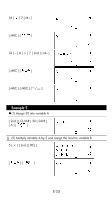
⇒ The SWAP command swaps the contents in two memory variables. Relational Operators The relational operators that can be used in FOR loops and conditional branching are: = = (equal to), < (less than), > (greater than), ≠ (not equal to), ≤ (less than or equal to), ≥ (greater than or equal to). Creating a New Program 1. Select NEW from the program menu and press [ ]. 2. Select the calculation mode you want the program to run in and press [ ]. 3. Select one of the ten program areas (P0123456789) and press [ ]. 4. Enter your program's commands. • You can enter the calculator's regular functions as commands. • To enter a program control instruction, press [ 2nd ] [ INST ] and make your selection. • To enter a space, press [ ALPHA ] [ SPC ]. 5. A semicolon (;) indicates the end of a command. To enter more than one command on a command line, separate them with a semicolon. For example: Line 1: INPUT A ; C = 0.5 × A ; PRINT " C = " , C ; END You can also place each command or group of commands on a separate line, as follows. In this case, a trailing semicolon can be omitted. Line 1: INPUT A ; C = 0.5 × A [ ] Line 2: PRINT " C = " , C ; END Executing a Program 1. When you finish entering or editing a program, press [ / CL ESC ] to return to the program menu, select RUN and press [ ]. (Or you can press [ PROG ] in MAIN mode.) 2. Select the relevant program area and press [ ] to begin executing the program. 3. To re-execute the program, press [ ] while the program's final result is on the display. 4. To abort the execution of a program, press [ / CL ESC ]. A message appears asking you to confirm that you want to stop the execution. STOP : N Y Press [ ] to move the cursor to Y and then press [ ]. E-29