HP DL165 Technologies for HP ProLiant 100-series G5 (Generation 5) servers, 2n - Page 4
AMD Opteron™ processors - proliant g5 server series
 |
UPC - 884962026601
View all HP DL165 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 4 highlights
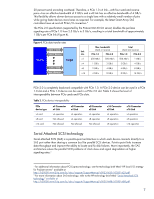
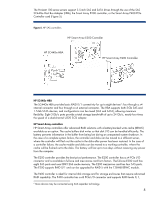
AMD Opteron™ processors AMD Opteron multi-core processors include Direct Connect™ and HyperTransport™ technology. Their method of parallel, point-to-point interconnectivity provides scalable bandwidth among the processor, I/O subsystem, and chipset.2 Opteron processors have an integrated memory controller that directly supports PC2-6400 (DDR2-800) DIMMs. The AMD architecture replaces the FSB with direct communication links between each CPU, between CPU and I/O, and between CPU and memory. Select HP ProLiant 100-series servers support AMD Opteron quad-core processors. The dual-core AMD Opteron 1000 and 2200 series processors include a dedicated 1-MB L2 cache per core (Figure 3A). Second-generation Opteron 2200-series processors run at up to 3.0 GHz. The quad-core AMD Opteron 2300 processor (Figure 3B) includes a dedicated 512-KB L2 cache for each core and a 2-MB L3 cache shared by all cores. The quad-core AMD Opteron also uses Dual Dynamic Power Management™ architecture, a design that separates the core and memory power planes. Figure 3. Block diagrams of dual-core and quad-core AMD Opteron processors A. Dual-Core architecture B. Quad-Core architecture CPU0 CPU1 1 MB L2 Cache 1 MB L2 Cache System Request I/F Crossbar Switch DDR2 Memory Cntlr Hypertransport I/F CPU0 CPU1 CPU2 CPU3 512 KB L2 Cache 512 KB L2 Cache 512 KB L2 Cache 512 KB L2 Cache 2 MB L3 Cache System Request I/F Crossbar Switch DDR2 Memory Cntlr Hypertransport I/F 72-bi t 72-bi t Link 1 Link 2 Link 3 72-bi t 72-bit Link 1 Link 2 Link 3 ProLiant 100-series G5 servers that support the Opteron processor use a split-plane motherboard that separates the voltage feeds to the CPU core and the DDR2 memory controller. This split-plane design allows granular power management of the Opteron processor to reduce energy consumption while increasing performance. 2 For additional information about AMD processors, see the HP technology brief titled "The AMD processor roadmap for industry-standard servers" at http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00428708/c00428708.pdf 4