HP LaserJet 5200 HP LaserJet 5200 Series Printer - Software Technical Referenc - Page 124
Point and Print installation for Windows 98, Windows Me, Windows 2000, and Windows Serve ... - ps driver
 |
View all HP LaserJet 5200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 124 highlights
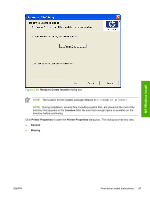
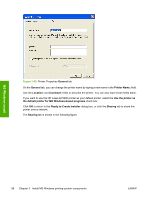
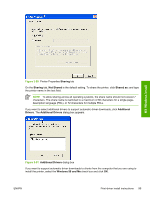
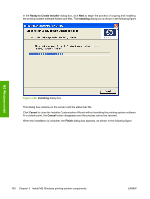
MS Windows install Point and Print installation for Windows 98, Windows Me, Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 The following information helps you install a print driver by using the Microsoft Point and Print function when you cannot see the device on the network. Point and Print is a Microsoft term that describes a two-step driver installation process. The first step is to install a shared driver on a network print server. The second step is to "point" to the print server from a network client so that the client can use the print driver. This section outlines the procedures for installing print drivers by using Point and Print. If these procedures are not successful, contact Microsoft. Hewlett-Packard provides drivers that are compatible with the Point and Print feature, but this is a function of the MS Windows operating systems, not of HP print drivers. Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 drivers from HP support only Intel X86 processor types. To install the print driver on a Windows 2000,Windows XP, or Windows Server 2003 operating system, you must have administrator privileges. To completely install the Windows 2000 print driver on the Windows 2000 server, you must have administrator privileges on the server. The Windows 2000 Printer .INF file must contain the same device name as the Windows 98 or Windows Me printer .INF file. Point and Print installation of a postscript driver is supported only with a Windows 98 or Windows Me PS Driver V4.0 or later. In a homogenous operating system environment (one in which all of the clients and servers are running in the same operating system), the same print driver version that is vended from the server to the clients in a Point and Print environment also runs and controls the print queue configuration on the server. However, in a mixed operating system environment (one in which servers and clients might run on different operating systems), conflicts can occur when client computers run a version of the print driver that is different from the one on the print server. In an effort to increase operating system stability, Microsoft determined that, starting with Windows 2000 and continuing with all future operating systems, print drivers would run as user-mode processes. Usermode drivers run in a protected part of the operating system, as do all of the normal end-user processes and software programs. A user-mode print driver that functions incorrectly can terminate (or "crash") only the process in which it is running-not the whole operating system. Because access to critical system resources is restricted, overall operating system stability is increased. www.techweb.boi.hp.com Set a default printer This section applies to the Windows 98, Windows Me, Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 operating systems. 1. In Windows 98, Windows Me, and Windows 2000, click Start, click Settings, and then click Printers. In Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, click Start, click Control Panel, and then click Printers and Faxes (Windows XP Professional) or Printers and other hardware devices (Windows XP Home). 2. Right-click the device that you want to set as the default printer. 3. Click Set As Default. A check mark appears next to the menu option. 102 Chapter 3 Install MS Windows printing-system components ENWW