HP ML150 HP Power Capping and Dynamic Power Capping for ProLiant servers techn - Page 5
Clock throttling - proliant g4
 |
UPC - 884420743644
View all HP ML150 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
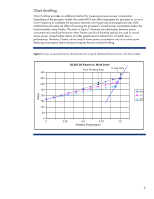
Clock throttling Clock throttling provides an additional method for lowering processor power consumption. Depending on the processor model, the system BIOS can either reprogram the processor to run at a lower frequency or modulate the processor between running periods and stopped periods. Both methods have the same net effect of lowering the processor's overall power consumption below the levels available using P-states. The chart in Figure 2 illustrates the relationship between power consumed and overall performance when P-states and clock throttling settings are used to control server power. Using P-states clearly provides greater power reduction for a smaller loss in performance. However, P-states can be used to lower power consumption only to a certain point. Reducing consumption below that point requires the use of clock throttling. Figure 2. Power versus performance characteristics for a typical Intel-based ProLiant server with three P-states WWaatttss DL360 G4 Power vs. Work Done Clock Throttling slope P-state slope 400 350 300 250 P0 200 P1 P2 150 100 50 0 0 500 100.0205 1500 200.050 2500 03.07050 3500 410.000 4500 RelativIPteeerPrafoetirromfnoasrmncaence 5