HP Workstation zx2000 HP OpenGL Implementation Guide for HP-UX 11.X (IPF versi - Page 41
rescaling normals, command are
 |
View all HP Workstation zx2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 41 highlights
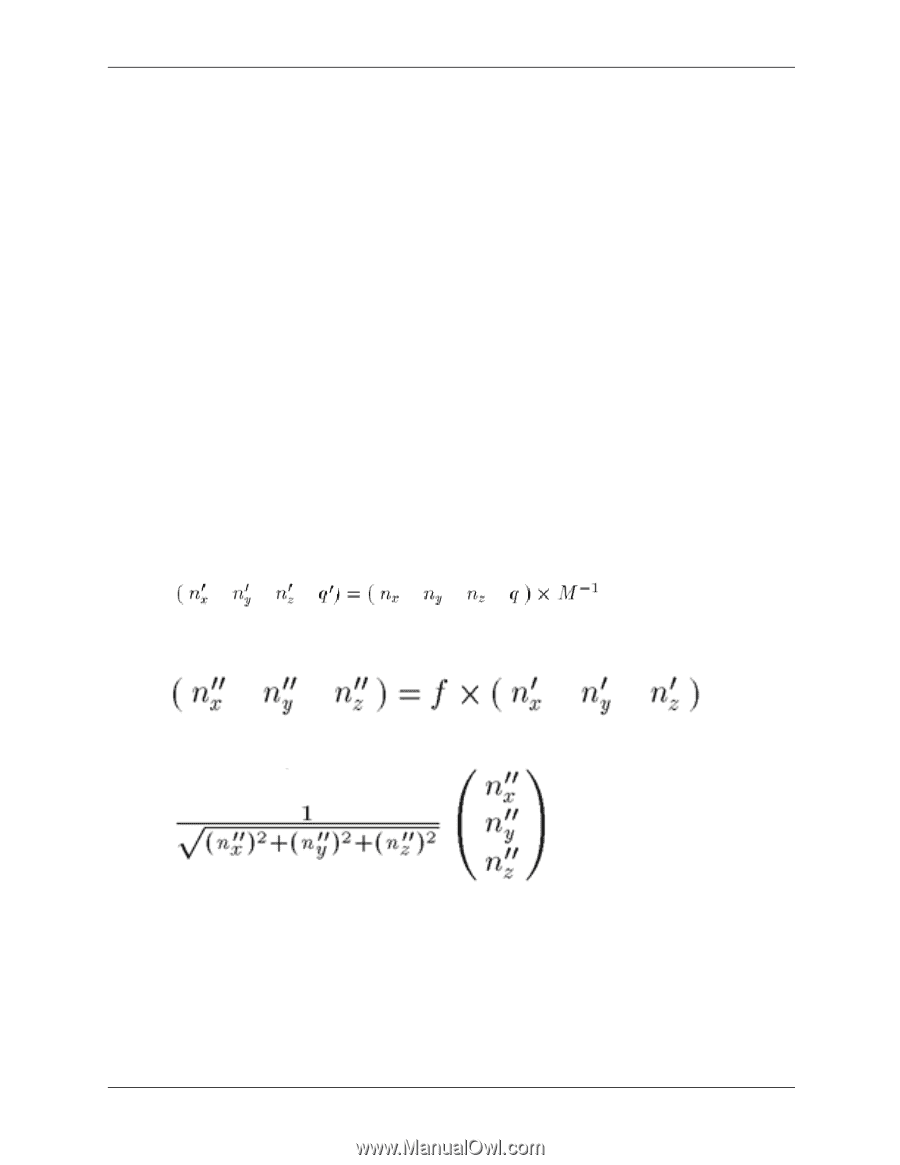
programming hints rescaling normals When normal rescaling is enabled, a new operation is added to the transformation of the normal vector into eye coordinates. The normal vector is rescaled after it is multiplied by the inverse modelview matrix and before it is normalized. The rescale factor is chosen so that in many cases, normal vectors with unit length in object coordinates will not need to be normalized as they are transformed into eye coordinates. HP's implementation of OpenGL 1.1 supports the GL_RESCALE_NORMAL_EXT token. It is accepted by the parameter of glEnable, glDisable, and glIsEnabled, and by the parameter of glGetBooleanv, glGetIntegerv, glGetFloatv, and glGetDoublev. Normals that have unit length when sent to the OpenGL, have their length changed by the inverse of the scaling factor after transformation by the model-view inverse matrix when the model-view matrix represents a uniform scale. If rescaling is enabled, then normals specified with the Normal command are rescaled after transformation by the ModelView Inverse. Normals sent to the OpenGL may or may not have unit length. In addition, the length of the normals after transformation might be altered due to transformation by the model-view inverse matrix. If normalization is enabled, then normals specified with the glNormal3 command are normalized after transformation by the model-view inverse matrix and after rescaling if rescaling is enabled. Normalization and rescaling are controlled with glEnable and glDisable with the target equal to NORMALIZE or RESCALE_NORMAL. This requires two bits of state. The initial state is for normals not to be normalized or rescaled. Therefore, if the modelview matrix is M, the transformed plane equation is: the rescaled normal is: and the fully transformed normal is: OpenGL implementation guide 5-7