HP rp7400 Hardware Manual - rp7400 - Page 55
ESD Requirements, Effect of humidity on ESD charge levels, <TABLE>, Static protection measures
 |
View all HP rp7400 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 55 highlights
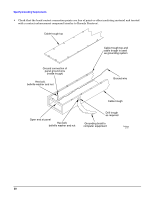
Determine the ESD Requirements Determine the ESD Requirements Static charges (voltage levels) occur when objects are separated or rubbed together. The voltage level of a static charge is determined by the following factors: • Types of materials • Relative humidity • Rate of change or separation Effect of humidity on ESD charge levels The table following lists charge levels based on personnel activities and humidity levels. Table 5 Personnel activitya Humidityband charge levels (voltages)c Person walking across a linoleum floor Person walking across a carpeted floor 26% 6,150 V 18,450 V 32% 5,750 V 17,250 V 40% 4,625 V 13,875 V 50% 3,700 V 11,100 V Person getting up from a plastic chair 24,600 V 23,000 V 18,500 V 14,800 V a. Source: B.A. Unger, Electrostatic Discharge Failures of Semiconductor Devices (Bell Laboratories, 1981) b. For the same relative humidity level, a high rate of airflow produces higher static charges than a low airflow rate. c. Some data in this table has been extrapolated. Static protection measures Follow these precautions to minimize possible ESD-induced failures in the computer room: • Maintain recommended humidity level and airflow rates in the computer room. • Install conductive flooring (conductive adhesive must be used when laying tiles). • Use conductive wax if waxed floors are necessary. • Ensure that all equipment and flooring are properly grounded and are at the same ground potential. • Use conductive tables and chairs. • Use a grounded wrist strap (or other grounding method) when handling circuit boards. • Store spare electronic modules in antistatic containers. 55