Lexmark MX826 Printer Languages and Interfaces Technical Reference - Page 143
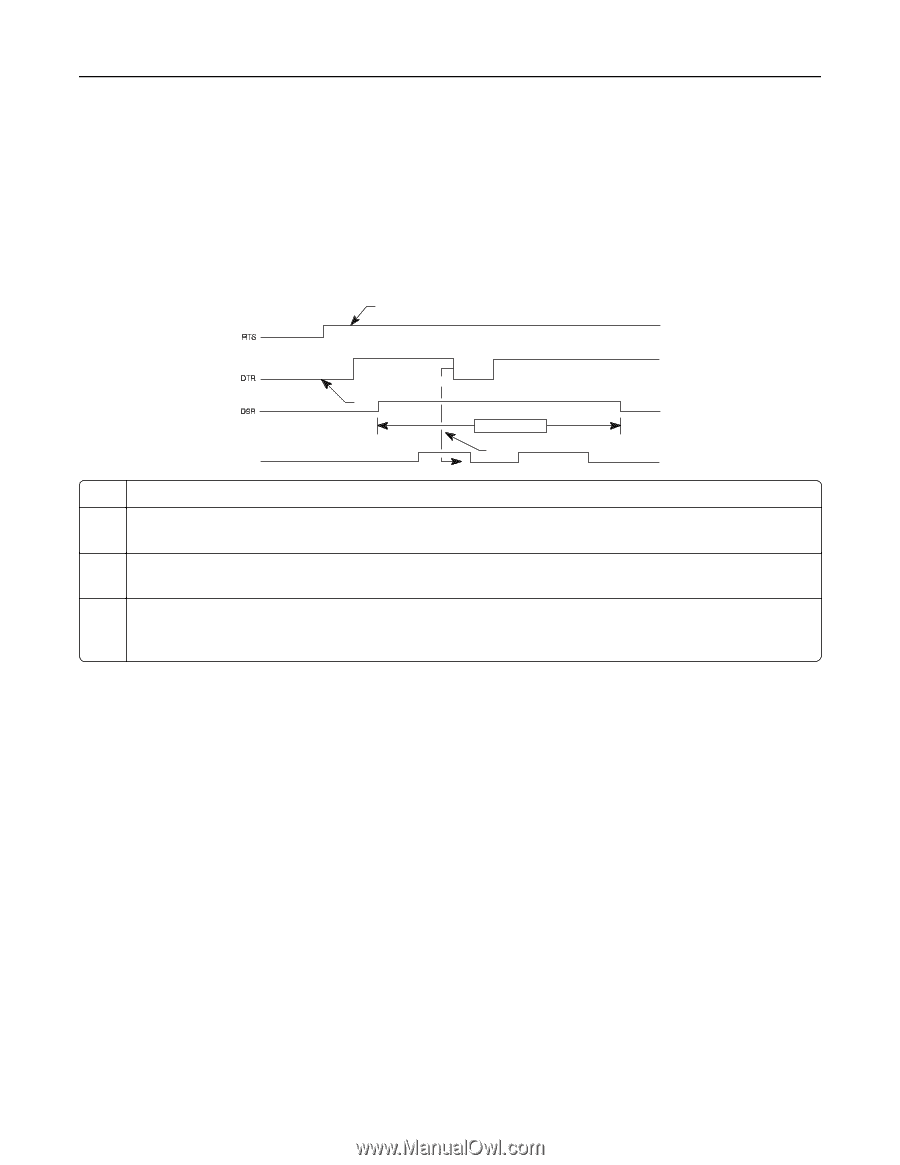
DTR and DTR/DSR protocol timing RS-232C, XON/XOFF protocol timing RS-232C
 |
View all Lexmark MX826 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 143 highlights
Printer interfaces 143 DTR and DTR/DSR protocol timing (RS-232C) Use DTR to pace the data flow from the computer. DTR goes from high to low to indicate to the computer that the printer cannot receive more data when it detects the following busy conditions: • Buffer full • Attendance error • Printer not in ready state The following diagram illustrates DTR Protocol Timing. 1 2 RXD 3 Receive Data Valid 4 1 The RTS signal is driven active as long as power is supplied to the printer. 2 The DTR signal becomes active when initialization is complete, telling the computer that the printer is ready to receive data. 3 When Honor DSR is On, the printer considers data received invalid when DSR is low and discards the data. Only DTR/DSR is used for flow control from the printer to the host computer. 4 DTR drops to tell the computer that the receive buffer is nearly full or that the printer is busy and that data transmission should stop. About 640 free bytes remain in the buffer at this time. If the computer continues to send data after the printer has sent a low DTR signal, then data could be lost. XON/XOFF protocol timing (RS-232C) When you select this data flow control protocol, the printer sends an XOFF signal when it detects the following busy conditions: • Buffer full • Attendance error • Printer not in ready state The following diagram illustrates XON/XOFF Protocol Timing.