Netgear MA521 MA521 Reference Manual - Page 21
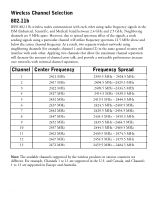
Wireless Channel Selection, Channel, Center Frequency, Frequency Spread
 |
UPC - 606449028713
View all Netgear MA521 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
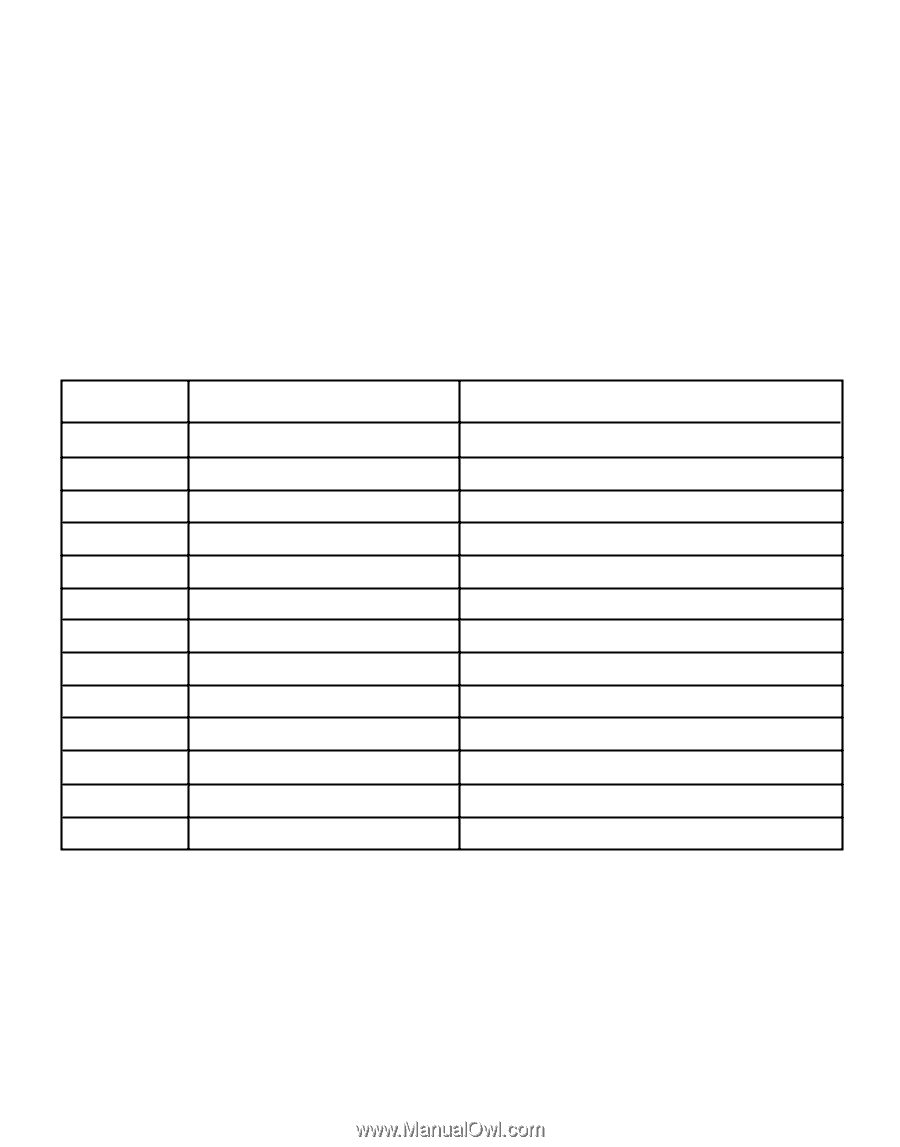
Wireless Channel Selection 802.11b IEEE 802.11b wireless nodes communicate with each other using radio frequency signals in the ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band between 2.4 GHz and 2.5 GHz. Neighboring channels are 5 MHz apart. However, due to spread spectrum effect of the signals, a node sending signals using a particular channel will utilize frequency spectrum 12.5 MHz above and below the center channel frequency. As a result, two separate wireless networks using neighboring channels (for example, channel 1 and channel 2) in the same general vicinity will interfere with each other. Applying two channels that allow the maximum channel separation will decrease the amount of channel cross talk, and provide a noticeable performance increase over networks with minimal channel separation. Channel Center Frequency Frequency Spread 1 2412 MHz 2 2417 MHz 3 2422 MHz 4 2427 MHz 5 2432 MHz 6 2437 MHz 7 2442 MHz 8 2447 MHz 9 2452 MHz 10 2457 MHz 11 2462 MHz 12 2467 MHz 13 2472 MHz 2399.5 MHz - 2424.5 MHz 2404.5 MHz -2429.5 MHz 2409.5 MHz -2434.5 MHz 2414.5 MHz -2439.5 MHz 2419.5 MHz - 2444.5 MHz 2424.5 MHz -2449.5 MHz 2429.5 MHz -2454.5 MHz 2434.5 MHz - 2459.5 MHz 2439.5 MHz -2464.5 MHz 2444.5 MHz -2469.5 MHz 2449.5 MHz - 2474.5 MHz 2454.5 MHz - 2479.5 MHz 2459.5 MHz - 2484.5 MHz Note: The available channels supported by the wireless products in various countries are different. For example, Channels 1 to 11 are supported in the U.S. and Canada, and Channels 1 to 13 are supported in Europe and Australia. 20