Netgear RT338 RT338 Reference Manual - Page 94
Using FirstGear to Con Internet Access, Table 5-6., Ethernet Tab Fields continued
 |
UPC - 606449004250
View all Netgear RT338 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 94 highlights
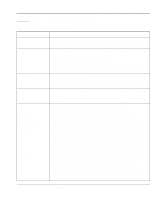
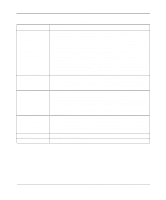
Reference Guide for the Model RT338 ISDN Router Table 5-6. Ethernet Tab Fields (continued) Field RIP Direction RIP Version DHCP Role Starting address Count Description Use this field to set how the router handles RIP (Routing Information Protocol): • If set to Both (default), the router broadcasts its routing table on the LAN and incorporates RIP broadcasts by other routers into its routing table. • If set to In Only, the router does not broadcast its routing table on the LAN. • If set to Out Only, the router broadcasts its routing table but ignores any RIP broadcast packets that it receives. • If set to None, the router does not participate in any RIP exchange with other routers. Usually, you should leave this parameter at its default of Both and let RIP propagate the routing information automatically. Use this box to determines how the router handles RIP (Routing Information Protocol). Your choices are: • RIP-1-The router accepts and sends RIP-1 messages only. • RIP-2B-The router accepts RIP-1 and RIP-2 messages (both broadcast and multicast) and sends RIP-2 messages in broadcast format. • RIP-2M-The router accepts RIP-1 and RIP-2 messages (both broadcast and multicast) and sends RIP-2 messages in multicast format. Among other improvements, RIP-2 supports subnetting and multicasting. For most applications, NETGEAR recommends the RIP-2B version. Select RIP-1 if other connected routers or workstations have problems with RIP-2. Select RIP-2M only in a pure RIP-2 environment. Use these radio buttons to configure the DHCP functionality of the router. When configured as a DHCP server, the router dynamically assigns IP addresses, netmasks, and DNS server addresses to PCs on the LAN. It also assigns its own LAN IP address as the default gateway of the PC. Your choices are: • None-Disables DHCP. • Server-Configures the router to acts as DHCP server. • Relay-Configures the router to obtain DHCP information from a Remote DHCP server and distribute that information to the local hosts. Use this field to specify the beginning address of the pool of addresses that the router assigns to attached hosts. If you are not assigned a range of addresses by an ISP or system administrator, NETGEAR recommends that you use addresses from the IETF-designated private addresses (for example, 192.168.x.x or 10.x.x.x) and select NAT for ISP or Remote Node Connections. This field is disabled unless DHCP Role is set to Server. Use this field to specify how many sequential addresses, beginning with the Starting Address, are available to be assigned to attached PCs. The maximum is 32. This field is disabled unless DHCP Role is set to Server. 5-18 Using FirstGear to Configure Internet Access