Poulan PRRT850 User Manual - Page 11
CULTIVATING, TILLING HINTS, TINE SHEAR PINS, with throttle in slow position mid-way - parts manual
 |
View all Poulan PRRT850 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
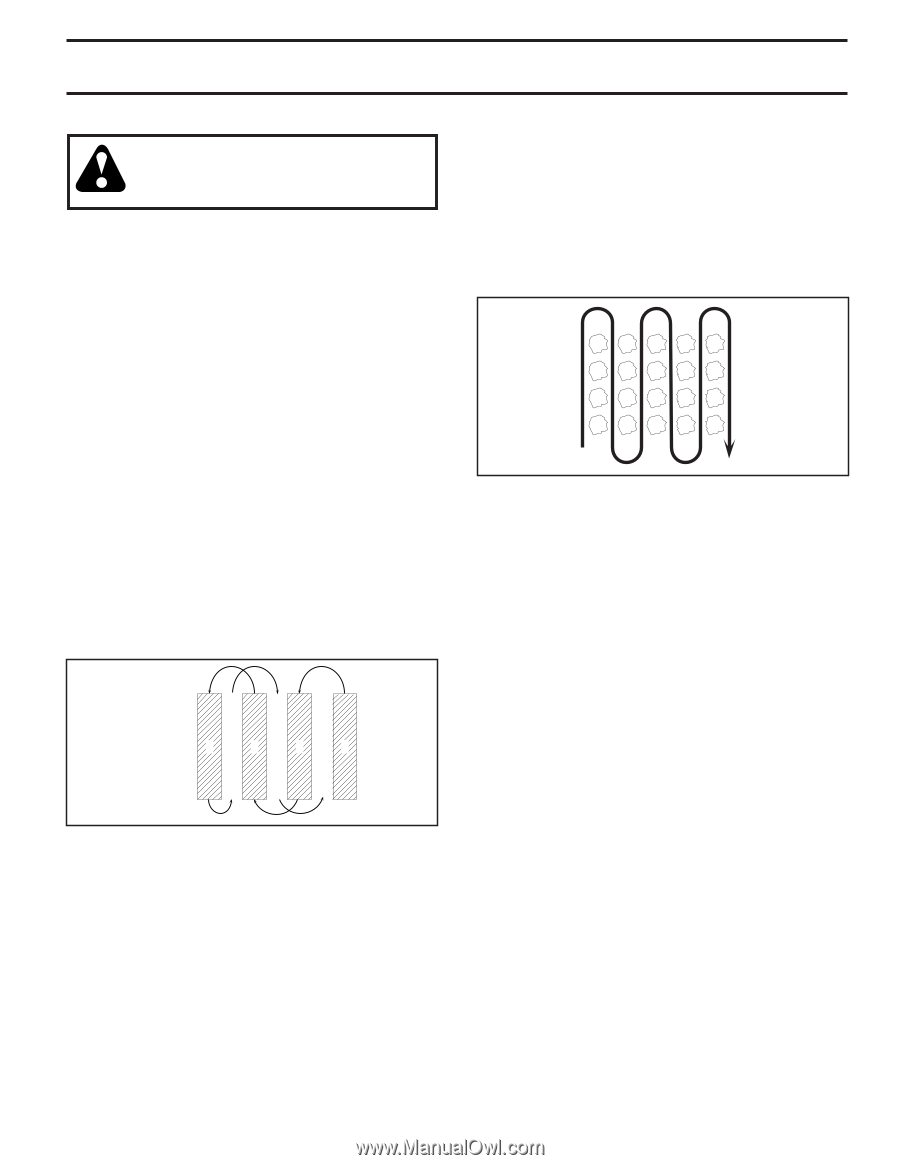
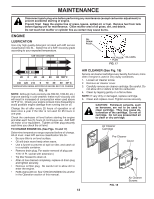
OPERATION TILLING HINTS CAUTION: Until you are accustomed to handling your tiller, start actual field use with throttle in slow position (mid-way between "FAST" and "IDLE"). • Tilling is digging into, turning over, and breaking up packed soil before planting. Loose, unpacked soil helps root growth. Best tilling depth is 4" to 6" (10-15 cm). A tiller will also clear the soil of unwanted vegetation. The decomposition of this vegetable matter enriches the soil. Depending on the climate (rainfall and wind), it may be advisable to till the soil at the end of the growing season to further condition the soil. • You will find tilling much easier if you leave a row untilled between passes. Then go back between tilled rows. (See Fig. 14) There are two reasons for doing this. First, wide turns are much easier to negotiate than about-faces. Second, the tiller won't be pulling itself, and you, toward the row next to it. • Soil conditions are important for proper tilling. Tines will not readily penetrate dry, hard soil which may contribute to excessive bounce and difficult handling of your tiller. Hard soil should be moistened before tilling; however, extremely wet soil will "ball-up" or clump during tilling. Wait until the soil is less wet in order to achieve the best results. When tilling in the fall, remove vines and long grass to prevent them from wrapping around the tine shaft and slowing your tilling operation. • Do not lean on handle. This takes weight off the wheels and reduces traction. To get through a really tough section of sod or hard ground, apply upward pressure on handle or lower the depth stake. CULTIVATING Cultivating is destroying the weeds between rows to prevent them from robbing nourishment and moisture from the plants. At the same time, breaking up the upper layer of soil crust will help retain moisture in the soil. Best digging depth is 1" to 3" (2.5-7.5 cm). Lower the outer side shields to protect small plants from being buried. • Cultivate up and down the rows at a speed which will allow tines to uproot weeds and leave the ground in rough condition, promoting no further growth of weeds and grass (See Fig. 15). FIG. 15 TINE SHEAR PINS The tine assemblies on your tiller are secured to the tine shaft with shear pins (See "TINE REPLACEMENT" in the Service and Adjustments section of this manual). If the tiller is unusually overloaded or jammed, the shear pins are designed to break before internal damage occurs to the transmission. • If shear pin(s) break, replace only with those shown in the Repair Parts section of this manual. 4 3 2 1 5 6 7 FIG. 14 11