TP-Link TD-W9960 TD-W9960EU V1 User Guide - Page 70
Interface Grouping, Advanced, Network, Dynamic DNS., DDNS service provider, Log in, For example
 |
View all TP-Link TD-W9960 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 70 highlights
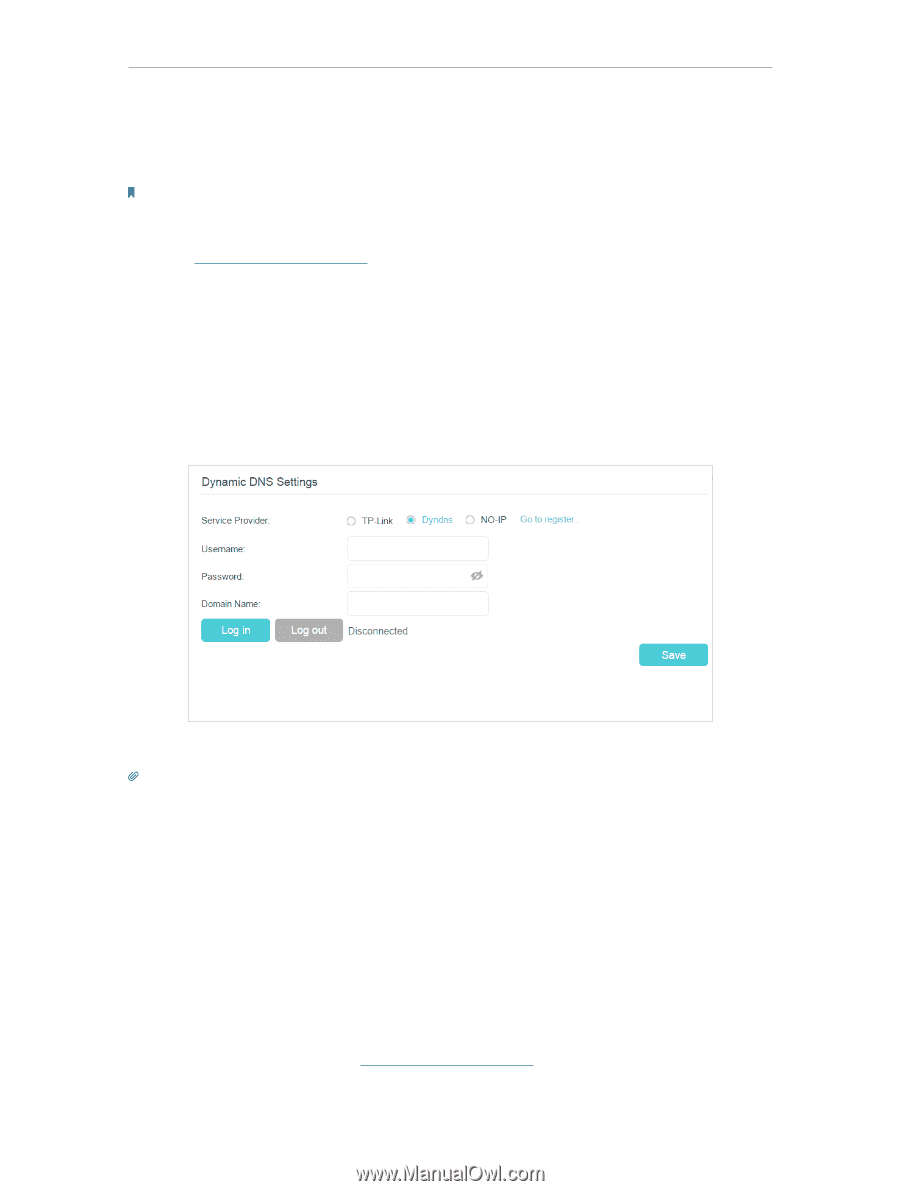
Chapter 13 Specify Your Network Settings the DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name Server) feature on the router to allow you and your friends to access your router and local servers (FTP, HTTP, etc.) using domain name, in no need of checking and remembering the IP address. Note: DDNS does not work if the ISP assigns a private WAN IP address (such as 192.168.1.x) to the modem router. To set up DDNS, please follow the instructions below: 1. Visit http://tplinkmodem.net, and log in with the account you set for the router. 2. Go to Advanced > Network > Dynamic DNS. 3. Select the DDNS service provider (TP-Link, Dyndns or NO-IP). 4. To use TP-Link DDNS service, you should log in with your TP-Link ID. 5. If you choose other DDNS service, you should also log in with your DDNS account, select a service provider and click Go to register ... Enter the username, password and domain name of the account (such as lisa.ddns.net). 6. Click Log in and Save. Tips: If you want to use a new DDNS account, please Logout first, then login with the new account. 13. 5. Interface Grouping I want to: How can I do that? Divide my devices connected to the modem router into different groups and disallow devices' cross-group communication. For example, in my house, devices connected to LAN1 and LAN3 are for work, while others for entertainment. i want to isolate the devices I use for work whilst keeping all devices' access to the internet. 1. Visit http://tplinkmodem.net, and log in with the account you set for the router. 66