TP-Link TL-WN822N User Guide - Page 29
TL-WN822N, Power Save Mode, Maximum, Normal, Network Type, Infrastructure, Ad-Hoc, Wireless Mode, - 300 mbps
 |
UPC - 845973050542
View all TP-Link TL-WN822N manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
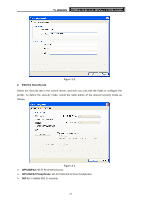
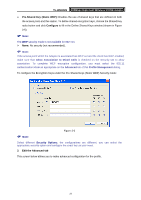
TL-WN822N 300Mbps High Gain Wireless N USB Adapter Figure 3-6 ¾ Power Save Mode - Please select the power save mode in the drop-down list. • Maximum - Selects maximum mode to let the access point buffer incoming messages for the Adapter. The Adapter will detect the access point if any messages are waiting periodically. • Normal - Normal mode uses maximum when retrieving a large number of packets, then switches back to power save mode after retrieving the packets. • Off - Turns power saving off, thus powering up the Wireless CardBus Adapter continuously for a short message response time. ¾ Network Type: There are basically two modes of networking: • Infrastructure - All wireless clients will connect to an access point or wireless router. • Ad-Hoc - Directly connecting to another computer, for peer-to-peer communication, using wireless network adapters on each computer, such as two or more TL-WN822N wireless adapters. ) Note: 1) An Infrastructure network contains an Access Point or wireless router. All the wireless devices or clients will connect to the wireless router or access point. 2) An Ad-Hoc network contains only clients, such as laptops with wireless desktop adapters. All the adapters must be in Ad-Hoc mode to communicate. ¾ Wireless Mode: Specifies 2.4 GHz 300 Mbps, 2.4 GHz 54 Mbps or 2.4 GHz 11 Mbps operation in an access point network. The Wireless adapter must match the wireless mode of the access point with which it associates. ¾ Wireless Mode when Starting an Ad Hoc Network: Specifies 2.4 GHz 300/54/11 Mbps to start an Ad Hoc network if no matching network name is found after scanning all available modes. This mode also allows the selection of the channel that the Wireless Adapter uses. The channels available depend on the regulatory domain. If the adapter finds no other ad hoc adapters, the channel that the adapter starts the ad hoc network with 23