TRENDnet TEW-639GR User Guide - Page 13
Clone Your PC's MAC Address - will not connect to network
 |
UPC - 710931600520
View all TRENDnet TEW-639GR manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
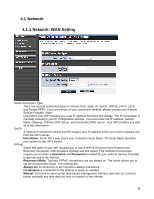
WAN MTU Setting The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is a parameter that determines the largest packet size (in bytes) that the router will send to the WAN. If LAN devices send larger packets, the router will break them into smaller packets. Ideally, you should set this to match the MTU of the connection to your ISP. Typical values are 1500 bytes for an Ethernet connection and 1492 bytes for a PPPoE connection. If the router's MTU is set too high, packets will be fragmented downstream. If the router's MTU is set too low, the router will fragment packets unnecessarily and in extreme cases may be unable to establish some connections. In either case, network performance can suffer. t modes. MAC Address Clone Each networking device has it's own unique MAC address defined by the hardware manufacturer. Some ISP's may check your computer's MAC address. Some ISP's record the MAC address of the network adapter in the computer or router used to initially connect to their service. The ISP will then only grant Internet access to requests from a computer or router with this particular MAC address. This router has a different MAC address than the computer or router that initially connected to the ISP. If you need to change the MAC address of the rounter's WAN-side Ethernet interface, either type in an alternate MAC address (for example, the MAC address of the router initially connected to the ISP) or copy the MAC address of a PC. To copy the MAC address of the computer that initially connected to the ISP, connect to the router using that computer and click the Clone Your PC's MAC Address button. The WAN interface will then use the MAC address of the network adapter in your computer. 13