TRENDnet TEW-P11G User's Guide - Page 53
Network Type, Ad-hoc, Infrastructure, Security, Disabled, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, Authentication, Bits/ - wireless wpa2
 |
UPC - 710931600568
View all TRENDnet TEW-P11G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 53 highlights
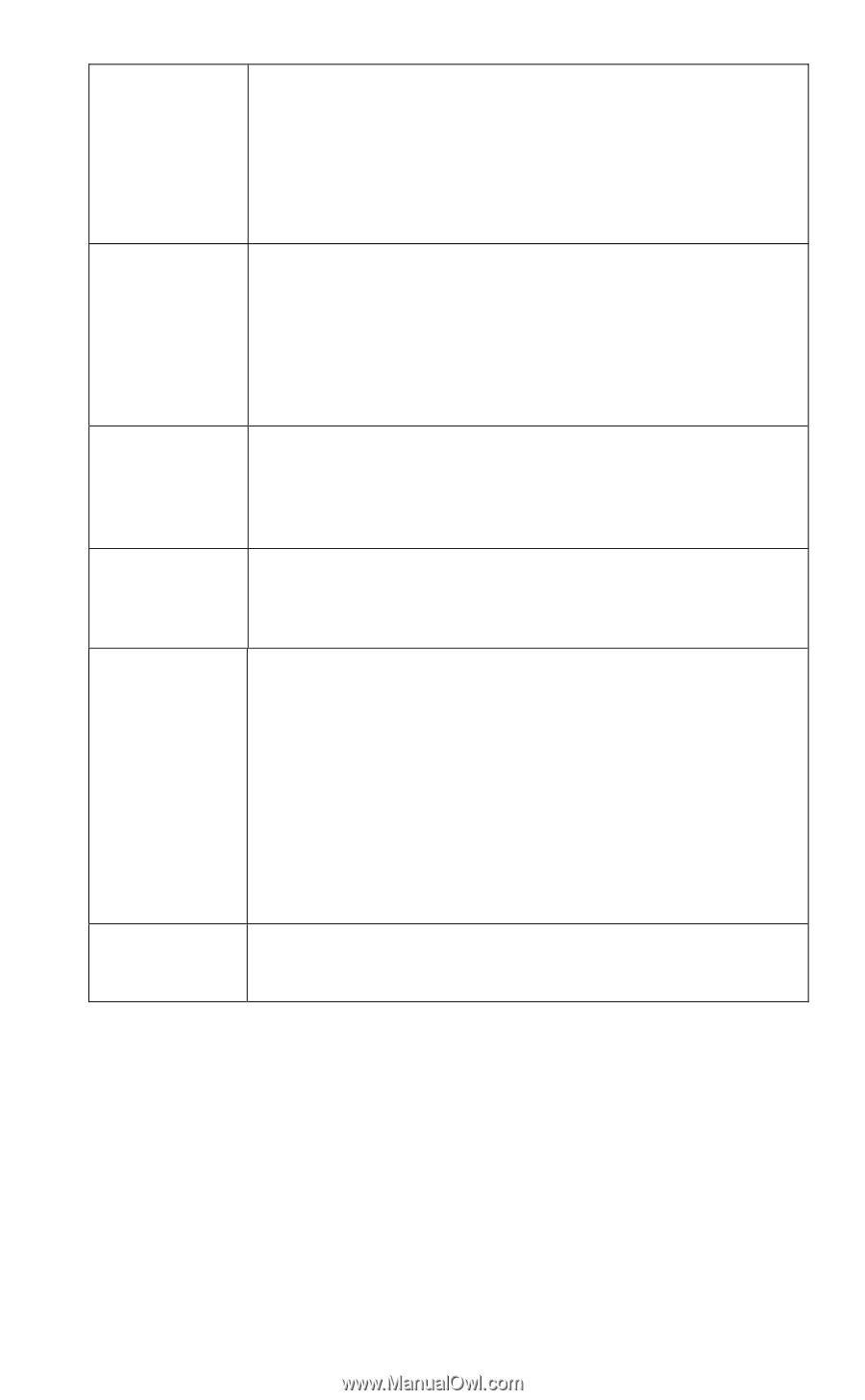
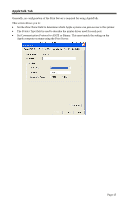
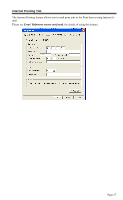
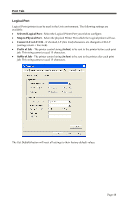
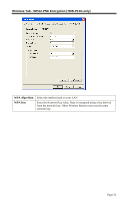
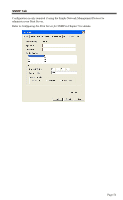
Network Type Security WEP Authentication 64 Bits/128Bits Key Table Default Key Select the correct value for your Wireless LAN. • Ad-hoc mode is used when there is no Wireless Access Point, and each Wireless station communicates directly with other Wireless stations. This is the older standard. • Infrastructure mode is used when each Wireless station connects to the Wireless Access point. This also provides access to the wired LAN. • Disabled - no data encryption is used. • WEP - data is encrypted using the WEP standard. • WPA-PSK - data is encrypted using the WPA-PSK standard. This is a later standard than WEP, and provides much better security than WEP. • WPA2-PSK -this is a further development of WPA-PSK, and offers even greater security. Options are "Open System" or "Shared Key". Select the method (Open System or Shared Key) used by other Wireless Stations. Shared Key is more secure than Open System. Select "64Bits" or "128Bits" as required to match other Wireless stations on your WLAN. Stations which do not have matching settings will be unable to communicate. 128 bit Keys are more secure than 64 bit Keys. Enter the key values to match other Wireless stations on your WLAN. This table is used when Encrypting and Decrypting data. All stations always transmit data encrypted using their default key (see below). The key number (1, 2, 3, 4) is also transmitted. The receiving station will use the key number (1, 2, 3, 4) to determine which key value to use for decryption. If the key value does not match the transmitting station, decryption will fail. The easiest way to ensure there are no problems is to have every Station, including the Access Point, use the same key table (all entries identical). Then, it does not matter which key is used as the default key. Select the key you wish to be the default. Transmitted data is ALWAYS encrypted using the Default Key; the other Keys are for decryption only. Page 50