Yamaha CVP-900 Owner's Manual - Page 156
Using the USB terminal on your computer with a USB/MIDI interface (UX256/UX96/ UX16, etc.) - clavinova electric piano
 |
View all Yamaha CVP-900 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 156 highlights
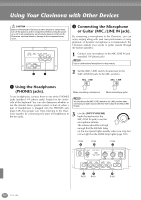
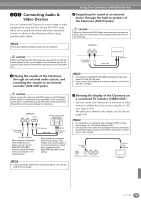
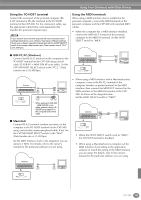
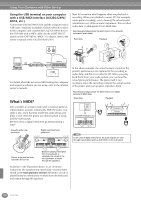
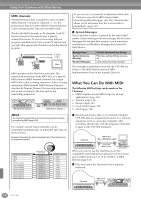
Using Your Clavinova with Other Devices Using the USB terminal on your computer with a USB/MIDI interface (UX256/UX96/ UX16, etc.) Connect the UX256/UX96/UX16 and the computer with a USB cable. Install the included UX256/UX96/UX16 driver to the computer, and connect the UX256/UX96/UX16 to the CVP-900 with a MIDI cable. Set the HOST SELECT switch on the CVP-900 to "MIDI." For details, refer to the owner's manual of the UX256/UX96/UX16. Now let's examine what happens when we play back a recording. When you playback a music CD (for example, a solo piano recording), you're hearing the actual sound (vibrations in air) of the acoustic instrument. This is called audio data, to distinguish it from MIDI data. Recording and playing back the performance of an acoustic instrument (audio data) Recording Playback IN OUT MIDI NEC MultiSync PC-9821 AS USB cable NEC Personal computer USB interface MIDI IN MIDI OUT Clavinova Mac MIDI PC-1 PC-2 For details about the necessary MIDI settings for computer and sequence software you are using, refer to the relevant owner's manuals. What's MIDI? Let's consider an acoustic piano and a classical guitar as representative acoustic instruments. With the piano, you strike a key, and a hammer inside hits some strings and plays a note. With the guitar, you directly pluck a string and the note sounds. But how does a digital instrument go about playing a note? Acoustic guitar note production Digital instrument note production In the above example, the actual acoustic sounds of the pianist's performance are captured in the recording as audio data, and this is recorded to CD. When you play back that CD on your audio system, you can hear the actual piano performance. The piano itself is not necessary, since the recording contains the actual sounds of the piano, and your speakers reproduce them. Recording and playing back the performance of a digital instrument (MIDI data) Recording Playback Controller (keyboard, etc.) FD Tone generator Sequencer FD L Internal amp Tone generator Internal amp (Electric circuit) R In the case of digital instruments, the audio signals are sent through output jacks (such as AUX OUT) on the instrument. Pluck a string and the body resonates the sound. Playing the keyboard Based on playing information from the keyboard, a sampled note stored in the tone generator is played through the speakers. As shown in the illustration above, in an electronic instrument, the sampled note (previously recorded note) stored in the tone generator section (electronic circuit) is played based on information received from the keyboard, and output through the speakers. 156 CVP-900