3Com 3C17300A Implementation Guide - Page 36
IGMP Multicast Filtering, Enabling IGMP Multicast Learning - switch interface ip
 |
UPC - 662705493169
View all 3Com 3C17300A manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 36 highlights
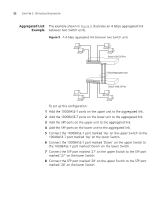
36 CHAPTER 3: USING MULTICAST FILTERING command will configure the Switch 4200 Series to automatically negotiate with compatible devices on VLAN 1 to become the querier. The Switch 4200 Family is compatible with any device that conforms to the IGMP v2 protocol. IGMP Multicast Filtering IGMP is the system that all IP-supporting network devices use to register endstations with multicast groups. It can be used on all LANs and VLANs that contain a multicast capable IP router and on other network devices that support IP. IGMP multicast filtering works as follows: 1 The IP router (or querier) periodically sends query packets to all the endstations in the LANs or VLANs that are connected to it. If your network has more than one IP router, then the one with the lowest IP address becomes the querier. The Switch can be the IGMP querier and will become so if its own IP address is lower than that of any other IGMP queriers connected to the LAN or VLAN. However, as the Switch only has an IP address on its default VLAN, the Switch will only ever query on the default VLAN (VLAN1). Therefore, if there are no other queriers on other VLANs, the IP multicast traffic will not be forwarded on them. 2 When an IP endstation receives a query packet, it sends a report packet back that identifies the multicast group that the endstation would like to join. 3 When the report packet arrives at a port on a Switch with IGMP multicast learning enabled, the Switch learns that the port is to forward traffic for the multicast group and then forwards the packet to the router. 4 When the router receives the report packet, it registers that the LAN or VLAN requires traffic for the multicast groups. 5 When the router forwards traffic for the multicast group to the LAN or VLAN, the Switch units only forward the traffic to ports that received a report packet. Enabling IGMP Multicast Learning You can enable or disable multicast learning and IGMP querying using the snoopMode command on the CLI or the web interface. For more information about enabling IGMP multicast learning, please refer to the