Belkin F5D8053 User Manual - Page 24
Wired Equivalent Privacy WEP, Wireless Protected Access WPA
 |
View all Belkin F5D8053 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 24 highlights
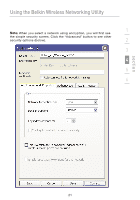
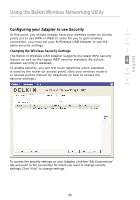
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a less secure, but more widely adopted wireless security protocol. Depending on the security level (64- or 128-bit), the user will be asked to input a 10- or 26-character hex key. A hex key is a combination of letters, a-f, and numbers, 0-9. Wireless Protected Access (WPA) is the new standard in the wireless security. However, not all wireless cards and adapters support this technology. Please check your wireless adapter's user manual to check if it supports WPA. Instead of a hex key, WPA uses only passphrases, which are much easier to remember. The following section, intended for the home, home-office, and small-office user, presents a few different ways to maximize the security of your wireless network. At the time of publication, four encryption methods are available: Encryption Methods: Name Acronym Security Features 64-bit Wired 128-bit Equivalent Privacy Encryption Wi-Fi Protected Access Wi-Fi Protected Access 64-bit WEP 128-bit WEP WPA-TKIP WPA-AES Good Better Best Best Static keys Static keys Dynamic key encryption and mutual authentication Dynamic key encryption and mutual authentication Encryption keys Added security based on RC4 over 64-bit algorithm (typically WEP using a 40-bit keys) key length of 104 bits, plus 24 additional bits of system- generated data TKIP (temporal AES key integrity (Advanced protocol) Encryption added so Standard) that keys are does not rotated and cause any encryption is throughput strengthened loss WEP WEP is a common protocol that adds security to all Wi-Fi-compliant wireless products. WEP gives wireless networks the equivalent level of privacy protection as a comparable wired network. 22