D-Link DGS-6600-48TS Configuration Guide - Page 459
DHCP Server Screening, DHCP Server Screening Operating Concept
 |
View all D-Link DGS-6600-48TS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 459 highlights
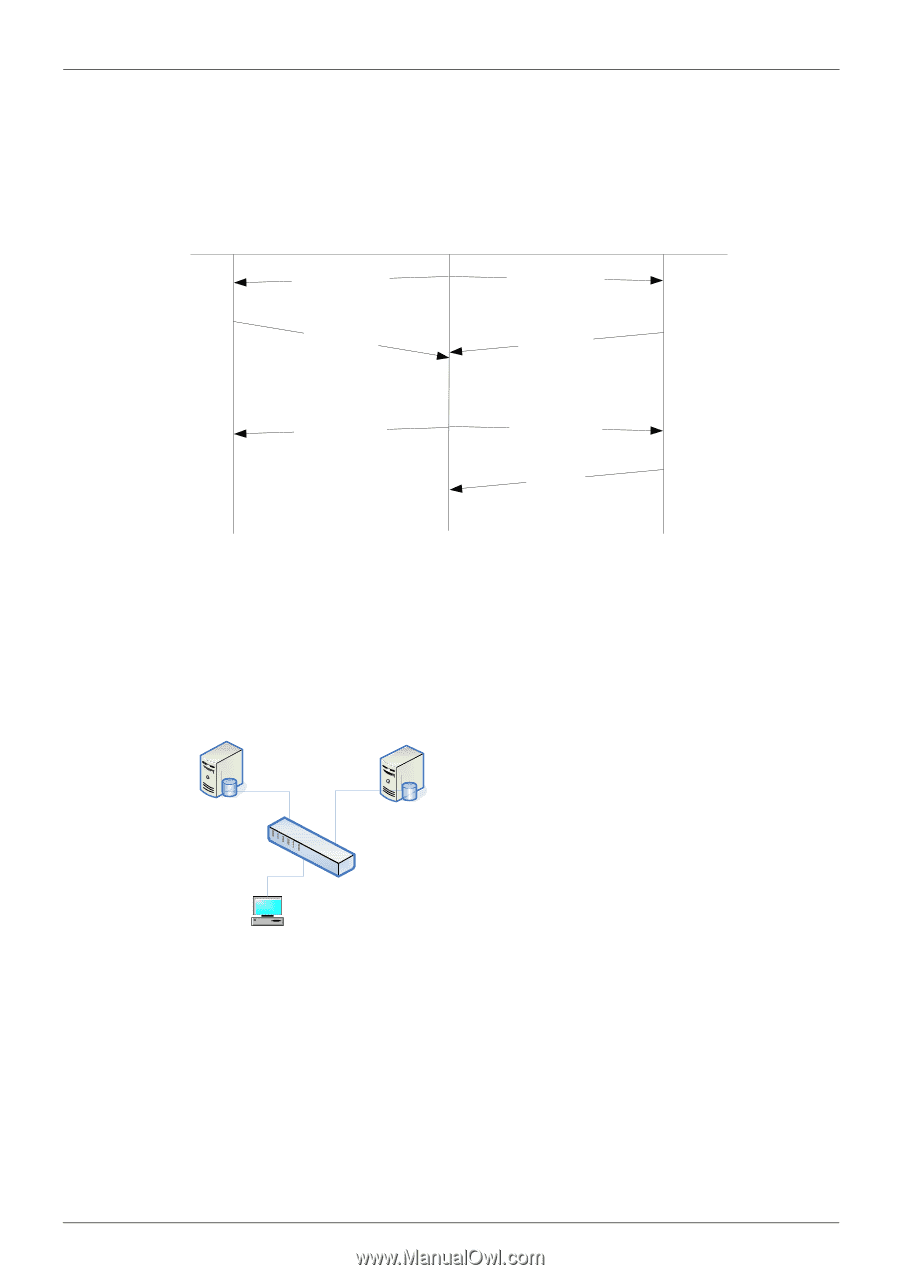
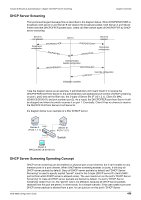
Volume 8-Security & Authentication / Chapter 43-DHCP Server Screening Chapter Overview DHCP Server Screening The typical exchanged message flow is described in the diagram below. When DHCPDISCOVER is broadcast, both server A and Server B will receive the broadcast packet, both Server A and Server B then send the DHCPOFFER packet back. Users can filter certain types of DHCPOFFER by DHCP server screening. Server A not selected Determines configuration DHCPDISCOVER DHCPOFFER Client X DHCPDISCOVER DHCPOFFER Server B selected Determines configuration Collects Replies Selects configuration DHCPREQUEST DHCPREQUEST Commits configuration DHCPACK Initialization complete Take the diagram above as an example, if administrators don't want Client X to receive the DHCPOFFER sent from Server A, the administrators can enable per port control of DHCP screening on port1, port2 and set the filter rule, the 3-tuple of Server B's IP (10.1.2.1), Client X's MAC (00:80:C8:00:00:01) and port number (port 2). As a result, the DHCPOFFER sent from Server A will be dropped and when the switch receives it on port 1. Eventually, Client X has no chance to receive the DHCPOFFER from Server A but Server B. the diagram below is an example of a filter DHSCP server. Server A Port 1 Server B IP(10.1.1.1) Port 2 IP(10.1.2.1) Port 3 Switch Client X MAC(00:80:c8:00:00:01) DHCP Server Screening Operating Concept DHCP server screening can be enabled on physical port or port channel, but it can't enable on any member ports of a port channel. When DHCPserver screening enables on ports, it will drop all DHCP server packets by default. Deny all DHCP server packets by default and "DHCP Server Screening" is used to specify explicit "permit" rules for the 3-tuple (DHCP server IP, client's MAC, port list from which DHCP server is allowed come). The user needs turn on the port's "DHCP Server Screening" to make all DHCP server packets are denied by default. If a port's "DHCP Server Screening" doesn't turn on, the "permit" rule is not effective, because all DHCP server packets received from this port are permit. In other words, for a simple scenario, if the user makes sure none DHCP server packets is allowed from a port, he can just turn on this port's "DHCP Server DGS-6600 Configuration Guide 459