| Section |
Page |
| Contents |
3 |
| Getting Help |
7 |
| • Using the Gateway Web�site |
7 |
| • Using Help and Support |
7 |
| • Using BigFix |
7 |
| • Using Your Computer guide |
7 |
| • Using Do More With Gateway |
7 |
| • Using online help |
7 |
| • Contacting Gateway |
7 |
| Thank you for purchasing our computer! |
8 |
| Gateway Web site |
9 |
| Using eSupport |
10 |
| Support Home |
10 |
| Product Support |
10 |
| Downloads |
10 |
| Contact Us |
10 |
| Account Info |
10 |
| PC Tools |
10 |
| Help and Support |
11 |
| To start Help and Support: |
11 |
| Searching for a topic |
12 |
| BigFix |
12 |
| To start BigFix: |
12 |
| To learn more about using BigFix: |
12 |
| Using Your Computer guide |
13 |
| To access the Using Your Computer guide: |
13 |
| Online help |
13 |
| Gateway contact information |
15 |
| • Identifying features |
15 |
| • Locating your computer model and serial number |
15 |
| • Locating the Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity |
15 |
| • Locating the specifications for your computer |
15 |
| • Purchasing accessories |
15 |
| Desktop PC Front |
16 |
| Important |
16 |
| Desktop PC Back |
18 |
| Important |
18 |
| Identifying your model |
21 |
| Important |
21 |
| Gateway model and serial number |
21 |
| Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity |
21 |
| Finding your specifications |
22 |
| Accessories |
22 |
| Memory |
22 |
| Printers |
23 |
| Storage Devices |
23 |
| USB flash drive |
23 |
| Uninterruptible power supplies |
23 |
| Getting Started |
25 |
| • Using your computer safely |
25 |
| • Protecting your computer from power source problems |
25 |
| • Turning your computer on and off |
25 |
| • Adjusting the volume |
25 |
| • Using the keyboard and the mouse |
25 |
| • Using the computer display |
25 |
| • Installing peripheral devices |
25 |
| Working safely |
26 |
| Reducing eye strain |
26 |
| Setting up your computer desk and chair |
26 |
| Setting up your computer and computer accessories |
27 |
| Sitting at your computer |
27 |
| Avoiding discomfort and injury from repetitive strain |
27 |
| Protecting from power source problems |
28 |
| Warning |
28 |
| Checking the voltage selection |
28 |
| Caution |
28 |
| To set the voltage selection switch: |
29 |
| Starting your computer |
29 |
| To start your computer: |
29 |
| 1 Connect the cables to your computer. See the setup poster. |
29 |
| 2 Turn on your computer. |
29 |
| 3 If you are starting your computer for the first time, follow the on-screen instructions to set ... |
29 |
| 4 Turn on any peripheral devices, such as printers or scanners, and see the documentation that ca... |
29 |
| Waking up your computer |
30 |
| Tips & Tricks |
30 |
| Turning off your computer |
30 |
| Warning |
30 |
| To turn off your computer: |
30 |
| 1 Click Start, then click Turn Off Computer. The Turn Off Computer dialog box opens. |
30 |
| 2 Click Turn Off. Windows shuts down and turns off your computer. |
30 |
| Important |
30 |
| Restarting (rebooting) your computer |
31 |
| To close unresponsive programs and restart your computer: |
31 |
| 1 Press Ctrl+Alt+Del. The Task Manager window opens. |
31 |
| 2 Click the Applications tab, then click the program that is not responding. |
31 |
| 3 Click End Task. |
31 |
| 4 Click X in the top-right corner of the Windows Task Manager dialog box. |
31 |
| 5 If your computer does not respond, turn it off, wait ten seconds, then turn it on again. |
31 |
| Important |
31 |
| Adjusting the volume |
31 |
| To adjust the overall volume level using hardware controls: |
31 |
| Tips & Tricks |
31 |
| Using the keyboard |
32 |
| Keyboard features |
32 |
| Using the mouse |
34 |
| Tips & Tricks |
35 |
| Connecting the modem |
36 |
| Warning |
36 |
| To connect the modem: |
36 |
| 1 Insert one end of the modem cable into the modem jack��on the back of your computer. |
36 |
| 2 Insert the other end of the modem cable into a telephone wall jack. The modem will not work wit... |
36 |
| 3 Start your computer, then start your communications program. |
36 |
| Connecting to a wired Ethernet network |
37 |
| Important |
37 |
| To connect to a wired Ethernet network: |
37 |
| 1 Insert one end of the network cable into the network jack��on the back of your computer. |
37 |
| 2 Insert the other end of the network cable into a network jack. |
37 |
| Tips & Tricks |
37 |
| Installing a printer, scanner, or other peripheral device |
38 |
| Important |
38 |
| Help and Support |
38 |
| Using Drives and Ports |
39 |
| • Using the diskette drive |
39 |
| • Using the memory card reader |
39 |
| • Using CD or DVD drives |
39 |
| Using the diskette drive |
40 |
| To use a diskette: |
40 |
| 1 Insert the diskette into the diskette drive with the label facing up. |
40 |
| 2 To access a file on the diskette, click Start, then click My Computer. Double-click the diskett... |
40 |
| 3 To remove the diskette, make sure that the drive activity light is off, then press the diskette... |
40 |
| Using the memory card reader |
40 |
| Memory card types |
41 |
| Inserting a memory card |
41 |
| Caution |
41 |
| To use a memory card: |
41 |
| 1 Insert the memory card into the memory card slot as indicated in the previous table. |
41 |
| 2 To access a file on the memory card, click Start, then click My Computer. Double-click the driv... |
41 |
| To remove a memory card: |
42 |
| Caution |
42 |
| Important |
42 |
| Using the CD or DVD drive |
43 |
| Identifying drive types |
43 |
| Inserting a CD or DVD |
44 |
| Important |
44 |
| To insert a CD or DVD: |
44 |
| 1 Press the eject button on the CD or DVD drive. |
44 |
| 2 Place the disc in the tray with the label facing up. |
44 |
| Important |
44 |
| 3 Press the eject button to close the tray. |
44 |
| Playing a CD |
44 |
| Tips & Tricks |
45 |
| Playing a DVD |
45 |
| Tips & Tricks |
45 |
| Creating CDs and DVDs |
45 |
| Tips & Tricks |
45 |
| Maintaining Your Computer |
47 |
| • Caring for your computer |
47 |
| • Updating Windows |
47 |
| • Protecting your computer from viruses |
47 |
| • Cleaning your computer |
47 |
| • Restoring your system |
47 |
| • Opening the computer case |
47 |
| • Adding memory and replacing the battery |
47 |
| Caring for your computer |
48 |
| Updating Windows |
48 |
| To run Windows Update: |
48 |
| 1 Connect to the Internet. |
48 |
| 2 Click Start, All Programs, then click Windows Update. |
48 |
| 3 Click Scan for Available Updates. |
48 |
| Help and Support |
48 |
| Protecting your computer from viruses |
49 |
| Help and Support |
49 |
| To scan for viruses: |
49 |
| 1 Click Start, All Programs, Norton AntiVirus, then click Norton AntiVirus�2004. Norton AntiVirus... |
49 |
| 2 Click Scan for Viruses. |
50 |
| 3 Click the type of scan you want to make in the Scan for Viruses area, then under Actions, click... |
50 |
| To remove a virus: |
50 |
| 1 If Norton AntiVirus finds a virus, follow all on-screen instructions to remove the virus. |
50 |
| 2 Turn off your computer and leave it off for at least 30�seconds. |
50 |
| 3 Turn on your computer and rescan for the virus. |
50 |
| To update Norton AntiVirus: |
51 |
| Tips & Tricks |
51 |
| 1 Make sure that you are connected to the Internet. |
51 |
| 2 Click Start, All Programs, Norton AntiVirus, then click LiveUpdate - Norton AntiVirus. The Live... |
51 |
| 3 Follow the on-screen instructions to update your Norton AntiVirus program with the latest virus... |
51 |
| 4 When the program has finished, click Finish. |
51 |
| Cleaning your computer |
51 |
| Cleaning the exterior |
51 |
| Warning |
51 |
| Cleaning the keyboard |
52 |
| Cleaning the computer display |
52 |
| Caution |
52 |
| Cleaning the mouse |
52 |
| To clean your optical mouse: |
52 |
| To clean your trackball mouse: |
53 |
| 1 Turn the mouse upside down. |
53 |
| 2 Rotate the retaining ring on the bottom of the mouse counter-clockwise, then remove the retaini... |
53 |
| 3 Remove any dust, lint, or dirt from the mouse ball with a soft cloth. |
53 |
| 4 Clean the mouse rollers with a cotton swab dipped in isopropyl alcohol. |
53 |
| 5 Replace the mouse ball and lock the retaining ring into place. |
53 |
| Cleaning CDs or DVDs |
54 |
| Restoring your system |
54 |
| Preventing static electricity discharge |
55 |
| Warning |
55 |
| Caution |
55 |
| Warning |
55 |
| Opening the case |
56 |
| Warning |
56 |
| Removing the side panel |
56 |
| To remove the side panel: |
56 |
| 1 Follow the instructions in “First steps” on page�60. |
56 |
| 2 Shut down your computer, then disconnect the power cord and modem, network, and all peripheral ... |
56 |
| 3 Press the power button to drain any residual power from your computer. |
56 |
| 4 Remove the two thumbscrews from the side panel cover, slide the side panel cover toward the bac... |
56 |
| Removing the front bezel |
57 |
| To remove the front bezel: |
57 |
| Caution |
57 |
| Closing the case |
58 |
| Replacing the side panel |
58 |
| To replace the side panel: |
58 |
| 1 Make sure that all of the internal cables are arranged inside the case so they will not be pinc... |
58 |
| 2 Align the side panel, then slide the side panel toward the front of the computer to secure it i... |
58 |
| 3 Replace the side panel thumbscrews. |
58 |
| 4 Reconnect the cables and power cord. |
58 |
| Replacing the front bezel |
59 |
| To replace the front bezel: |
59 |
| 1 Align the latch pins with the computer latch holes. |
59 |
| 2 Press the bezel firmly into place. |
59 |
| Installing memory |
60 |
| To install or replace DIMM memory: |
60 |
| 1 Remove the side panel by following the instructions in “Removing the side panel” on page�50. |
60 |
| 2 For more stability, place your computer on its side. To avoid scratching the case, place it on ... |
60 |
| 3 Find the memory module banks on your system board. |
60 |
| Important |
60 |
| 4 If you are removing a DIMM from the memory module bank, gently pull the plastic tabs away from ... |
61 |
| 5 Align the notches on the new DIMM with the notches on the memory module bank and press the modu... |
61 |
| 6 Replace the side panel by following the instructions in “Replacing the side panel” on page�52. |
61 |
| 7 Return your computer to its upright position. |
61 |
| 8 Reconnect the cables and the power cord. |
61 |
| 9 Turn on your computer. Windows starts and the Windows desktop appears. |
61 |
| 10 Click Start, Control Panel, then click Performance and Maintenance (if in Category view). Clic... |
61 |
| Replacing the system battery |
62 |
| Warning |
62 |
| To replace the battery: |
62 |
| 1 Restart your computer. |
62 |
| 2 During the restart, press and hold the F1 key. The main menu of the BIOS�Setup�utility opens. |
62 |
| 3 Write down all the values in the menus and submenus, then exit from the utility. |
62 |
| 4 Shut down your computer. |
62 |
| 5 Remove the side panel by following the instructions in “Removing the side panel” on page�50. |
62 |
| 6 For more stability, place your computer on its side. To avoid scratching the case, place it on ... |
62 |
| 7 Locate the old battery on the system board and note its orientation. You will need to install t... |
62 |
| 8 Push the battery release tab. The battery pops out of the socket. |
62 |
| Important |
63 |
| 9 Make sure that the positive (+) side of the new battery is facing up, then press the battery in... |
63 |
| 10 Replace the side panel by following the instructions in “Replacing the side panel” on page�52. |
63 |
| 11 Reconnect all external cables and the power cord. |
63 |
| 12 Turn on your computer. |
63 |
| 13 Open the BIOS Setup utility. |
63 |
| 14 In the BIOS Setup utility, restore any settings that you wrote down in Step�3. |
63 |
| 15 Save all your settings and exit the BIOS Setup utility. |
63 |
| Troubleshooting |
65 |
| • Troubleshooting typical hardware and software problems |
65 |
| • Getting telephone support |
65 |
| • Using automated troubleshooting systems |
65 |
| • Getting tutoring and training |
65 |
| Safety guidelines |
66 |
| Warning |
66 |
| First steps |
66 |
| Help and Support |
66 |
| Troubleshooting |
67 |
| Add-in cards |
67 |
| The computer does not recognize an add-in card |
67 |
| Audio |
67 |
| Battery |
67 |
| CD or DVD drives |
67 |
| The computer does not recognize a disc or the CD or DVD drive |
67 |
| Audio CD does not produce sound |
68 |
| A DVD movie will not play |
68 |
| Computer |
69 |
| The computer will not start |
69 |
| Diskette drive |
69 |
| The diskette drive is not recognized |
69 |
| You cannot save a file to diskette or you see the message “disk is full or write-protected” |
69 |
| You see a “Access Denied” or “Write protect” error message |
69 |
| You see a “Disk is full” error message |
69 |
| You see a “Non-system disk” or “Disk error” error message |
70 |
| The diskette drive LED is lit continuously |
70 |
| DVD drives |
70 |
| File management |
70 |
| A file was accidentally deleted |
70 |
| To restore deleted files: |
70 |
| Help and Support |
70 |
| Hard drive |
71 |
| You see an “Insufficient disk space” error message |
71 |
| Caution |
71 |
| Help and Support |
71 |
| You see a “Data error” message |
71 |
| The hard drive cannot be accessed, or you see a “General failure reading drive C” error message |
71 |
| You see a “Non-system disk” or “disk error” error message |
71 |
| Internet |
72 |
| You cannot connect to the Internet |
72 |
| Help and Support |
72 |
| You see an “Unable to locate host” message and are unable to browse the Internet |
72 |
| Connecting to a Web site takes too long |
72 |
| People are sending you e-mail messages, but you have not received any mail |
73 |
| Keyboard |
73 |
| The keyboard does not work |
73 |
| A keyboard character keeps repeating or you see a “keyboard stuck” or “key failure” error message |
73 |
| Liquid spilled in the keyboard |
73 |
| Memory |
74 |
| You see a “Memory error” message |
74 |
| You see a “Not enough memory” error message |
74 |
| Help and Support |
74 |
| Memory card reader |
74 |
| Drive letters for the memory card slots do not appear in the My Computer window |
74 |
| Modem (dial-up) |
74 |
| Your modem does not dial or does not connect |
74 |
| To check the dialing properties: |
75 |
| Help and Support |
75 |
| You cannot connect to the Internet |
76 |
| Your 56K modem does not connect at 56K |
76 |
| Your fax communications program only sends and receives faxes at 14,400�bps when you have a 56K m... |
76 |
| The modem is not recognized by your computer |
76 |
| To run modem diagnostics: |
76 |
| Help and Support |
77 |
| The modem is noisy when it dials and connects |
77 |
| To turn down the modem volume: |
77 |
| Monitor |
77 |
| The screen resolution is not correct |
77 |
| Tips & Tricks |
77 |
| Tips & Tricks |
78 |
| Help and Support |
78 |
| The computer is running but there is no picture |
78 |
| The color is not uniform |
78 |
| Why is there a horizontal line or wire visible across the monitor screen? |
78 |
| The text on the display is dim or difficult to read |
79 |
| Tips & Tricks |
79 |
| Mouse |
79 |
| The mouse does not work |
79 |
| The mouse works erratically |
79 |
| Networks |
79 |
| You cannot connect to your company network |
79 |
| Help and Support |
80 |
| Passwords |
80 |
| Your computer does not accept your password |
80 |
| Power |
80 |
| Your computer will not turn on |
80 |
| Printer |
80 |
| The printer will not turn on |
80 |
| The printer is on but will not print |
80 |
| To set a default printer: |
81 |
| You see a “Printer queue is full” error message |
81 |
| To make sure that the printer is not set to work offline: |
81 |
| Help and Support |
81 |
| You see a “Printer is out of paper” error message |
81 |
| Sound |
82 |
| You are not getting sound from the speakers |
82 |
| Help and Support |
82 |
| Telephone support |
83 |
| Before calling Gateway Customer Care |
83 |
| Online Help |
83 |
| Printed documentation |
83 |
| The Microsoft Windows documentation |
83 |
| The software publisher’s Web site |
83 |
| Warning |
83 |
| Telephone numbers |
84 |
| Automated troubleshooting system |
84 |
| Telephone numbers |
84 |
| Self-help |
85 |
| Help and Support |
85 |
| Tutoring |
85 |
| Training |
85 |
| Networking Your Computer |
87 |
| • Introducing networking |
87 |
| • Creating an Ethernet network |
87 |
| • Testing your network |
87 |
| • Sharing your resources |
87 |
| • Troubleshooting your Ethernet network |
87 |
| Introduction to networking |
88 |
| Using a network |
88 |
| Sharing a single Internet connection |
88 |
| Sharing drives |
88 |
| Sharing peripheral devices |
88 |
| Streaming audio and video files |
88 |
| Playing multi-player games |
89 |
| Help and Support |
89 |
| Selecting a network connection |
89 |
| Wireless Ethernet network |
89 |
| Using a wireless Ethernet network |
89 |
| Warning |
89 |
| Important |
90 |
| Important |
90 |
| Wireless Ethernet speed and frequency |
90 |
| Important |
91 |
| Example access point router wireless Ethernet network |
91 |
| Tips & Tricks |
92 |
| Equipment you need for an access point wireless Ethernet network |
92 |
| Important |
93 |
| Tips & Tricks |
93 |
| Determining if wireless Ethernet is already installed on your computers |
93 |
| To determine if wireless Ethernet is already installed on your computer: |
93 |
| 1 Click Start, then click Control Panel. The Control Panel window opens. If your Control Panel is... |
93 |
| 2 Click/Double-click System, click the Hardware tab, then click Device Manager. The Device Manage... |
93 |
| 3 Click the plus (+) in front of Network adapters. The wireless Ethernet device installed in your... |
93 |
| Wired Ethernet network |
94 |
| Using a wired Ethernet network |
94 |
| Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, or Gigabit Ethernet |
94 |
| Important |
94 |
| Example router-based wired Ethernet network |
95 |
| Tips & Tricks |
95 |
| Equipment you need for a router-based wired Ethernet network |
95 |
| Important |
96 |
| Tips & Tricks |
96 |
| Determining if wired Ethernet is already installed on your computers |
96 |
| To determine if wired Ethernet is already installed on your computer: |
96 |
| 1 Click Start, then click Control Panel. The Control Panel window opens. If your Control Panel is... |
96 |
| 2 Click/Double-click System, click the Hardware tab, then click Device Manager. The Device Manage... |
96 |
| 3 Click the plus (+) in front of Network adapters. The wired Ethernet device installed in your co... |
96 |
| Creating an Ethernet network |
96 |
| Installing Ethernet cards and drivers |
96 |
| Making sure your broadband connection works |
97 |
| Important |
97 |
| Important |
97 |
| Naming the computers and the workgroup |
97 |
| Important |
97 |
| To identify this computer on the network: |
97 |
| 1 Click Start, then click Control Panel. The Control Panel window opens. If your Control Panel is... |
97 |
| 2 Click/Double-click System. The System Properties dialog box opens. |
97 |
| 3 Click Computer Name. |
97 |
| 4 Click Change. The Computer Name Changes dialog box opens. |
97 |
| 5 Type a unique computer name in the Computer name box. This name identifies the computer to othe... |
97 |
| 6 Type a name for your workgroup in the Workgroup box. Use a workgroup name of up to 15 character... |
97 |
| 7 Click OK to close the Computer Name Changes dialog box. |
97 |
| Configuring the TCP/IP protocol |
98 |
| Terms you should know |
98 |
| Using a DHCP server |
98 |
| To use a DHCP server |
98 |
| 1 Click Start, then click Control Panel. The Control Panel window opens. If your Control Panel is... |
98 |
| 2 Click/Double-click Network Connections. The Network Connections window opens. |
98 |
| 3 Right-click Local Area Connection, then click Properties. The Local Area Connection Properties ... |
99 |
| 4 Click to select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) check box in the This connection uses the follow... |
99 |
| 5 Click Properties. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box opens. |
99 |
| 6 Click the General tab. |
100 |
| 7 Click Obtain an IP address automatically. |
100 |
| 8 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box. |
100 |
| 9 Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box. |
100 |
| 10 Click X to close the Network Connections window. |
100 |
| 11 Repeat this procedure for every computer on your network. |
100 |
| Where to go from here |
100 |
| Setting up a wireless Ethernet network |
101 |
| Mounting the access point |
101 |
| Configuring the access point |
101 |
| Important |
101 |
| To configure the Linksys wireless access point router with 4-port switch: |
101 |
| 1 If you are connecting any wired devices to your wireless access point router, follow the instru... |
101 |
| 2 Plug one end of a straight-through cable into the WAN port on the wireless access point router ... |
101 |
| 3 Plug one end of the power adapter into the AC connector on the router and the other end into a ... |
101 |
| 4 Turn on the DSL or cable modem. |
101 |
| 5 Press the reset button on the wireless access point router. |
101 |
| 6 Temporarily connect a computer to the wireless access point router using a straight-through cab... |
101 |
| 7 From one of the computers plugged into your wireless access point router, open your Web browser. |
101 |
| 8 In the browser’s Address box, type http://192.168.1.1, then press Enter. |
102 |
| 9 When prompted for a username and password, leave the username box empty and type admin in the p... |
102 |
| 10 Enter the following values in the appropriate fields: |
102 |
| Host Name and Domain Name - Check with your ISP to see if entries are required in these fields an... |
102 |
| Enable/Disable wireless - Click Enable to turn on the wireless functions of your access point rou... |
102 |
| SSID - Type a unique name for your wireless access point. |
102 |
| Allow Broadcast SSID to associate - Clicking Yes lets you automatically see the SSID in the Avail... |
102 |
| Tips & Tricks |
102 |
| Channel - In the United States, you can specify any channel between 1 and 11. |
102 |
| WEP - To use WEP (wired equivalent privacy) encryption, select Mandatory. If you use WEP encrypti... |
102 |
| 11 Click Apply, then click Continue to save the settings. |
102 |
| 12 If you temporarily connected a computer to the access point router in Step�6, disconnect it. |
102 |
| 13 Reset the power on your cable or DSL modem. |
102 |
| 14 Restart all of your computers on the network. |
102 |
| 15 To connect to the access point, see “Connecting to an access point network” on page�97. |
102 |
| Connecting to an access point network |
103 |
| To connect to an access point wireless Ethernet network: |
103 |
| 1 Before connecting to an access point, you must turn on the wireless Ethernet emitter by clickin... |
103 |
| 2 Click/Double-click Network Connections. The Network Connections window opens. |
103 |
| 3 Right-click the Wireless Network Connection icon, then click View available wireless networks. ... |
103 |
| 4 Click the network you created in the Choose a wireless network list, then click Connect. Follow... |
103 |
| Help and Support |
104 |
| Configuring computer settings for an access point |
104 |
| To configure computer settings with WEP security for an access point wireless Ethernet network: |
104 |
| 1 With the Wireless Network Connection window open, click Change advanced settings. The Wireless ... |
104 |
| 2 Click the Wireless Networks tab. |
104 |
| 3 Click to select the access point network in the Preferred networks list, then click Properties.... |
105 |
| 4 Click the arrow button to open the Data encryption list, then click WEP. |
105 |
| 5 If the WEP network key is not provided automatically, click to clear The key is provided for me... |
105 |
| 6 Make sure that the This is a computer-to-computer (ad hoc) network; wireless access points are ... |
105 |
| 7 Click OK to close the Wireless Network Properties dialog box. Your network should be running. G... |
105 |
| Help and Support |
105 |
| Adding an access point |
106 |
| To manually add an access point wireless Ethernet network: |
106 |
| 1 With the Wireless Network Connection window open, click Change order of preferred networks. The... |
106 |
| 2 Click the Wireless Networks tab. |
106 |
| 3 Click Add. The Linksys properties dialog box opens. |
107 |
| 4 Type the name of the network in the Network name (SSID) box. |
107 |
| 5 Click the arrow button to open the Network Authentication list, then click the network authenti... |
107 |
| 6 If this is a security-enabled network, click the arrow button to open the Data encryption list,... |
107 |
| 7 If the WEP network key is not provided automatically, click to clear The key is provided for me... |
107 |
| 8 Make sure that the This is a computer-to-computer (ad hoc) network; wireless access points are ... |
107 |
| 9 Click OK to close the Wireless Network Properties dialog box. Your network should be running. G... |
107 |
| Help and Support |
108 |
| Setting up a wired Ethernet network |
108 |
| Important |
108 |
| Setting up a network using a router |
108 |
| To set up a network using a router: |
109 |
| 1 Plug one end of the power adapter into the AC connector on the router and the other end into a ... |
109 |
| 2 Turn on your computers. |
109 |
| 3 Plug one end of a straight-through network cable into any numbered port on the router (except t... |
109 |
| 4 Repeat Step�3 for each computer on the network. |
109 |
| 5 For an Internet connection, plug a straight-through cable into the WAN port on the router and t... |
110 |
| Configuring your router |
110 |
| Important |
110 |
| To configure the Linksys EtherFast Cable/DSL router: |
110 |
| 1 From one of the computers connected to the network, open your Web browser, type http://192.168.... |
110 |
| 2 When prompted for a username and password, leave the username box empty and type admin in the p... |
110 |
| 3 Enter the following values in the appropriate fields: |
110 |
| Router Name and Domain Name - Check with your ISP to see if entries are required in these fields ... |
110 |
| LAN IP Address - We recommend that you accept the defaults. |
110 |
| 4 When you are finished entering information on the Setup page, click Apply. |
110 |
| 5 Click the DHCP tab on the top of the screen. |
110 |
| 6 Click the Enable checkbox, then click Apply. |
110 |
| 7 Press the reset button on your cable or DSL modem, then restart the computer. Your network shou... |
110 |
| Testing your network |
111 |
| Sharing your resources |
112 |
| Sharing an Internet connection |
112 |
| Important |
112 |
| Important |
112 |
| To set up Internet Explorer on each computer on your Ethernet network: |
112 |
| 1 Make sure that the router or access point is turned on and configured as instructed by your cab... |
112 |
| 2 Click Start, right-click Internet, then click Internet Properties. The Internet Properties dial... |
112 |
| 3 Click the Connections tab. |
113 |
| 4 Click Setup. The New Connection Wizard opens. |
113 |
| 5 Click Next. The Network Connection Type screen opens. |
113 |
| 6 Click Connect to the Internet, then click Next. The Getting Ready screen opens. |
114 |
| 7 Click Set up my connection manually, then click Next. The Internet Connection screen opens. |
114 |
| 8 Click the type of Internet connection you are setting up, then click Next. |
114 |
| 9 Click Finish. |
114 |
| 10 Repeat this procedure for each computer on your network. Go to “Accessing the Internet” on pag... |
114 |
| Accessing the Internet |
115 |
| To access the Internet from your computer: |
115 |
| 1 Make sure that the router or access point is turned on. |
115 |
| 2 Open Internet Explorer and browse the Internet. |
115 |
| Sharing drives and printers |
115 |
| Important |
115 |
| Sharing drives or folders |
115 |
| To share drives or folders: |
115 |
| 1 Make sure that each computer on your network has Windows file and printer sharing turned on by ... |
115 |
| 2 In My Computer or Windows Explorer, right-click the drive or folder that you want to share, the... |
115 |
| 3 Click the Sharing tab. |
116 |
| 4 If this is the first time you have shared a drive or folder, click Network Setup Wizard to enab... |
116 |
| 5 Click OK. |
116 |
| Un-sharing drives, folders, and files |
117 |
| To un-share drives or folders: |
117 |
| 1 In My Computer or Windows Explorer, right-click the drive or folder that you want to un-share, ... |
117 |
| 2 Make sure that the Share this folder on the network check box is not selected. |
117 |
| 3 Click OK. |
117 |
| Sharing printers |
117 |
| To share printers: |
117 |
| 1 Click Start, then click Control Panel. The Control Panel window opens. If your Control Panel is... |
117 |
| 2 Click/Double-click the Printers and Faxes icon. The Printers and Faxes window opens. |
117 |
| 3 Right-click the name of the printer you want to share, then click Sharing. |
117 |
| 4 Click Share this printer. |
117 |
| 5 Click OK. |
117 |
| Using the network |
117 |
| Viewing shared drives and folders |
118 |
| To view shared drives and folders: |
118 |
| 1 Click Start, then click My Network Places. The My Network Places window opens. |
118 |
| 2 Click/Double-click Entire Network. The Entire Network window opens. If you do not see the conte... |
118 |
| 3 Double-click Microsoft Windows Network. |
118 |
| 4 Double-click the name of your workgroup. The names of each of the computers in your workgroup a... |
118 |
| 5 Double-click the name of the computer containing the drive or folder you want to view. All shar... |
118 |
| Mapping a network drive |
118 |
| To map a network drive: |
118 |
| 1 Locate the drive or folder by completing the steps in “Viewing shared drives and folders” on pa... |
118 |
| 2 Right-click the drive or folder, then click Map Network Drive. The Map Network Drive wizard opens. |
118 |
| 3 Click the arrow button to open the Drive list, then click the drive letter you want to map this... |
118 |
| 4 Click Reconnect at Logon if you want to reconnect to this drive or folder each time you log on ... |
118 |
| 5 Click Finish. |
118 |
| Opening files across the network |
119 |
| To open files across the network: |
119 |
| 1 Start the program for the file you want to open. |
119 |
| 2 Click File, then click Open. |
119 |
| 3 Browse to the network drive that contains the file you want to open. |
119 |
| 4 Double-click the folder containing the file, then double-click the file. |
119 |
| Copying files across the network |
119 |
| To copy files across the network: |
119 |
| 1 Click Start, then click My Computer. The My Computer window opens. |
119 |
| 2 Browse to the network drive that contains the file you want to copy. |
119 |
| 3 Browse to the file you want to copy. |
119 |
| 4 Click the file. |
119 |
| 5 Click Edit, then click Copy. |
119 |
| 6 Double-click the folder where you want to copy the file to. |
119 |
| 7 Click Edit, then click Paste. |
119 |
| Printing files across the network |
120 |
| Important |
120 |
| To print files across the network: |
120 |
| 1 Open the file you want to print. |
120 |
| 2 Click File, then click Print. |
120 |
| 3 Click the arrow button to open the printer name list, then click the network printer. |
120 |
| 4 Click OK. |
120 |
| Connecting to hotspots |
120 |
| Important |
120 |
| Caution |
120 |
| Troubleshooting Your Ethernet network |
121 |
| Wired Ethernet network |
121 |
| You cannot see the other computers on your network |
121 |
| The computer does not recognize an add-in Ethernet card |
121 |
| Your wired Ethernet network is running slower than you expect |
121 |
| Wireless Ethernet network |
122 |
| You turned the wireless on, but it takes a while to connect. |
122 |
| Your connection on the network seems intermittent. |
122 |
| Your wireless Ethernet network is running slower than you expect |
122 |
| Important |
122 |
| To check the signal strength of your wireless Ethernet network: |
122 |
| You are in a wireless network, you can see the network, but cannot communicate, send files, print... |
123 |
| You are in a wireless network, but no available networks are listed in the Windows XP Wireless Ne... |
123 |
| Your wireless network is listed as a preferred network, but it has an “x” on it. |
123 |
| Safety, Regulatory, and Legal Information |
125 |
| • Safety information |
125 |
| • Regulatory statements |
125 |
| • Notices |
125 |
| Important safety information |
126 |
| Warning |
126 |
| Setting up your system |
126 |
| Care during use |
126 |
| Replacement parts and accessories |
126 |
| Warning |
127 |
| Warning |
127 |
| Regulatory compliance statements |
127 |
| United States of America |
127 |
| Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Unintentional emitter per FCC Part�15 |
127 |
| California Proposition�65 Warning |
127 |
| Warning |
127 |
| Telecommunications per Part�68 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR�47) (applicable to product... |
128 |
| Canada |
128 |
| Industry Canada (IC) Unintentional emitter per ICES-003 |
128 |
| Telecommunications per Industry Canada CS-03 (for products fitted with an IC-compliant modem) |
128 |
| Warning |
129 |
| Laser safety statement |
129 |
| Warning |
129 |
| Television antenna connectors protection (for systems fitted with TV/cable TV�tuner cards) |
129 |
| External television antenna grounding |
129 |
| Lightning protection |
129 |
| Power lines |
130 |
| Warning |
130 |
| Notices |
131 |
| All Rights Reserved |
131 |
| Trademark Acknowledgments |
131 |
| Macrovision statement |
131 |
| Index |
133 |
| A |
133 |
| B |
133 |
| C |
133 |
| D |
134 |
| E |
135 |
| F |
135 |
| G |
135 |
| H |
135 |
| I |
136 |
| J |
136 |
| K |
136 |
| L |
136 |
| M |
136 |
| N |
137 |
| O |
137 |
| P |
138 |
| R |
138 |
| S |
138 |
| T |
139 |
| U |
140 |
| V |
140 |
| W |
140 |

 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61 62
62 63
63 64
64 65
65 66
66 67
67 68
68 69
69 70
70 71
71 72
72 73
73 74
74 75
75 76
76 77
77 78
78 79
79 80
80 81
81 82
82 83
83 84
84 85
85 86
86 87
87 88
88 89
89 90
90 91
91 92
92 93
93 94
94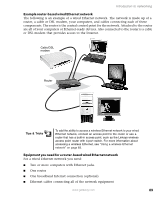 95
95 96
96 97
97 98
98 99
99 100
100 101
101 102
102 103
103 104
104 105
105 106
106 107
107 108
108 109
109 110
110 111
111 112
112 113
113 114
114 115
115 116
116 117
117 118
118 119
119 120
120 121
121 122
122 123
123 124
124 125
125 126
126 127
127 128
128 129
129 130
130 131
131 132
132 133
133 134
134 135
135 136
136 137
137 138
138 139
139 140
140 141
141 142
142 143
143 144
144