Gateway 838GM User Guide - Page 91
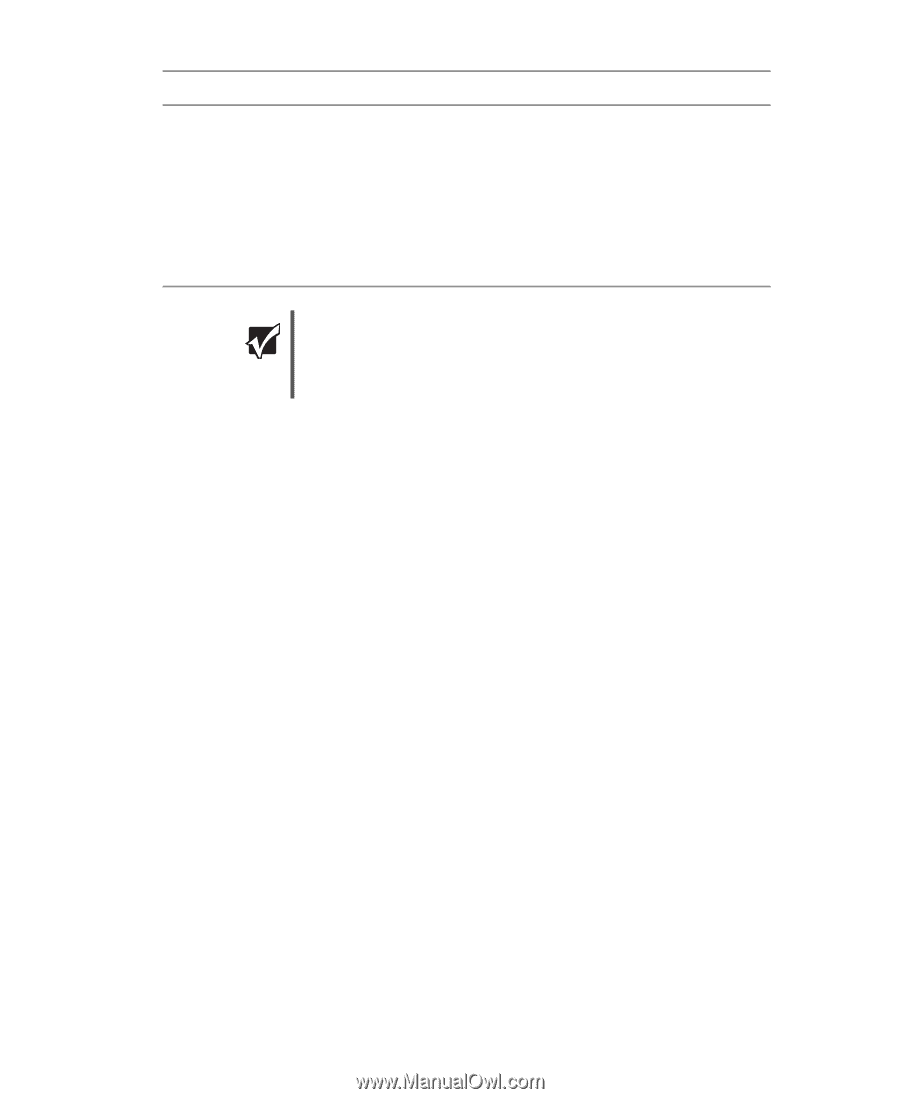
Example access point router wireless Ethernet network
 |
View all Gateway 838GM manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 91 highlights
Introduction to networking Network Type Speed Frequency Advantages Disadvantages IEEE 802.11g 54 Mbps 2.4 GHz ■ Compatible with IEEE 802.11b networks ■ Longer range (100 to 150 feet) than IEEE 802.11a ■ Possible interference from cordless telephones and microwaves ■ Not compatible with IEEE 802.11a networks Important The speed of a wireless network is related to signal strength. Signal strength is affected by the distance between your wireless network devices, by radio interference, and by interference from natural obstructions such as walls, floors, and doors. The most common way to set up a wireless Ethernet network is Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) using a wireless access point router. A DHCP network configuration uses an access point router to automatically assign IP addresses to each computer or network device. Example access point router wireless Ethernet network By using an access point, you can join a wireless Ethernet network and access a wired Ethernet network. The following is an example of an access point wireless Ethernet network that shows how an access point also lets you access the Internet. The network is made up of an access point, a cable or DSL modem, and your computers. The access point is the central control point for the network. Attached to the access point is the cable or DSL modem that provides access to the Internet. Each of the computers or Ethernet-ready devices communicate with the access point using radio waves. If your computer does not have a built-in wireless Ethernet emitter, you need to add a wireless PCI card (desktop), PC card (notebook), or USB adapter. www.gateway.com 85
-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144
 |
 |