Gateway P-6317 8513212 - Gateway Notebook Reference Guide with eRecovery R0 - Page 61
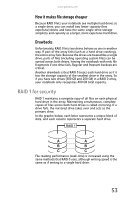
RAID 1 for security
 |
View all Gateway P-6317 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 61 highlights
www.gateway.com How it makes file storage cheaper Because RAID 0 lets your notebook see multiple hard drives as a single drive, you can install two lower capacity (less expensive) drives and have the same single-drive storage simplicity and capacity as a larger, more expensive hard drive. Drawbacks Unfortunately, RAID 0 lets two drives behave as one in another way. If part of the array fails (such as a hard drive crashing), the entire array fails. Because the drives are treated like a single drive, parts of files (including operating system files) can be spread across both drives, leaving the notebook with only file fragments if one drive fails. Regular and frequent backups are critical. Another drawback is that RAID 0 treats each hard drive as if it has the storage capacity of the smallest drive in the array. So if you have two drives (300 GB and 200 GB) in a RAID 0 array, your notebook only recognizes 400 GB total capacity. RAID 1 for security RAID 1 maintains a complete copy of all files on each physical hard drive in the array. Maintaining simultaneous, complete copies of files across both hard drives is called mirroring. If a drive fails, the mirrored drive takes over and acts as the primary drive. In the graphic below, each letter represents a unique block of data, and each column represents a separate hard drive. RAID 1 A A B B C C File reading performance (seek time) is increased using the same methods that RAID 0 uses, although writing speed is the same as if writing to a single hard drive. 53