HP ProLiant BL660c AMD Opteron™ and Intel® Xeon® x - Page 3
Microarchitecture
 |
View all HP ProLiant BL660c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
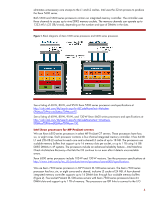
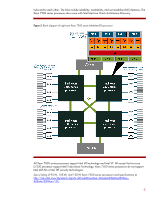
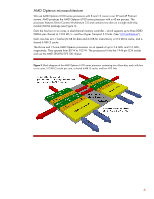
Xeon processor numbers may have an alpha prefix (for example, E5530) to indicate the power and performance level (Table 2). Table 2. Prefixes for Xeon processor sequences Prefix X E L Description Performance optimized Mainstream (rack optimized) Power optimized Microarchitecture Microarchitecture refers to the internal processor design, such as the number of cores, that implements an instruction set. AMD and Intel constantly increase the number of cores, but they differ in their approach to using them. AMD provides more processor cores to run multi-threaded applications, with each core executing a single thread. Intel increases processor utilization by using Hyper-Threading Technology to execute two threads per core. Intel Microarchitecture Nehalem Intel builds its Microarchitecture Nehalem on hafnium-based Hi-k metal gate silicon technology. This material reduces electrical leakage and allows for smaller, more energy-efficient, and higher performance processors. Nehalem-based Xeon 5500, 5600, and 7500 series processors support some or all of the following technologies: Three-level cache hierarchy supplies an on-die 64-KB L1 cache, an individual 256-KB L2 cache for each core, and a shared, inclusive L3 cache. An integrated memory controller provides high-speed channels to dedicated DDR3 memory sockets. Intel Hyper-Threading (HT) Technology improves processor utilization by letting each core execute two threads simultaneously. QuickPath links connect the processors and I/O chipset (see "I/O architecture"). Trusted Execution Technology (TXT) increases protection against software-based attacks (see "Data security"). Advanced Encryption Standard-New Instructions (AES-NI) allows fast and secure data encryption of a variety of applications. (See "Data security"). Turbo Boost Technology increases the clock frequency of all active cores when the processor operates below pre-set power and thermal design limits. It complements HT Technology. Intel Virtualization Technology (VT) helps hardware to reduce software virtualization overhead (see "Virtualization"). Dynamic Power Management works with Turbo Boost to increase performance and optimize the power use of the processor, chipset, and memory. Intel Xeon processors for 1P and 2P ProLiant servers We use Xeon 5500 and 5600 series processors in HP ProLiant 100 and 300 series servers. The Xeon 5500 series processor has six cores that share an 8-MB L3 cache. Intel uses the 45nanometer (nm) manufacturing process to produce the processor. By contrast, the Xeon 5600 series processor has eight-cores that share a 12 MB L3 cache (Figure 1). The L3 cache duplicates data in each core's L1 and L2 caches and stores it outside the cores. It also 3