HP ProLiant DL380p DDR3 memory technology
HP ProLiant DL380p Manual
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL380p manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
HP ProLiant DL380p manual content summary:
- HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 1
topology ...4 On-die Termination ...6 Address parity checking on RDIMMs 6 DIMM Temperature sensor ...6 DDR3 memory and NUMA systems architectures 7 Older server architectures ...7 DDR3 and the new systems architecture 8 DDR3 and Intel 4P architecture ...9 DDR3 and AMD 2P/4P systems architecture - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 2
with capacities as large as 64 GB. Types of DDR3 DIMMs DDR3 supports both Unbuffered and Registered DIMMs. With Unbuffered DIMMs (UDIMMs), all address FBDIMM architecture was primarily designed to increase the maximum memory for servers by allowing more DIMMs to be installed on each memory channel. - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 3
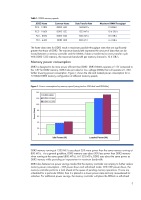
Table 1. DDR3 memory speeds JEDEC Name PC3 - 12800 PC3 - 10600 PC3 - 8500 PC3 - 6400 Common Name DDR3-1600 DDR3-1333 DDR3-1066 DDR3- 800 Data Transfer Rate 1600MT/s 1333 MT/s 1066 MT/s 800 MT/s Maximum DIMM Throughput 12.8GB/s 10.6 GB/s 8.5 GB/s 6.4 GB/s The faster data rates for DDR3 result in - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 4
from HP. At 1.35V, low-voltage DDR3 DIMMs cannot operate at full speed when the number of DIMMs installed per channel increases. Tables 2 and 3 summarize low-voltage DDR3 DIMM operation in ProLiant servers. Low-voltage DDR3 memory is not currently supported in the Intel-based 4P ProLiant G7 servers - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 5
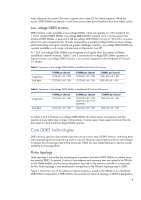
Command / Clock Bus Memory Controller DDR3 Fly-by Topology Data Data Address / Command / Clock Bus Memory Controller Fly-by topology solves the problem of the shrinking data-eye by eliminating the need to simultaneously deliver the data signals to each DRAM. With Fly-by topology, each command - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 6
itself (number of ranks) and its position on the memory channel. Both of these refinements contribute to the signal integrity improvements necessary to support the faster DDR3 speeds. Address parity checking on RDIMMs In DDR2, address parity detection was an optional feature. With DDR3, it is now - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 7
since their inception, using DDR1and later DDR2 memory. The new AMD-based ProLiant G7 servers continue to use a NUMA architecture that has been updated to support DDR3 memory. Intel-based HP ProLiant G6 and G7 servers now incorporate NUMA architecture along with other new features. The new - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 8
architecture, each memory channel has a maximum total raw bandwidth of 9.6 GB/s for systems supporting PC2-6400 fully buffered DIMMs. The memory channels of systems that use registered DIMMs can support a maximum bandwidth of 6.4 GB/s. With four memory channels per system, the theoretical maximum - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 9
for the Intel-based 2P ProLiant G6 servers has a maximum theoretical memory bandwidth of 64 GB/s, 65% greater than that of the older architecture using DDR2 memory. DDR3 and Intel 4P architecture Figure 6 shows the processor/memory architecture for the 4P HP ProLiant G7 servers that use Intel Xeon - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 10
memory configurations, including a fully populated system. DDR3 and AMD 2P/4P systems architecture AMD-based HP ProLiant servers have used NUMA architecture since their inception. The ProLiant G7 servers are the first generation to use DDR3 memory. Figure 7 shows processor/memory architecture for an - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 11
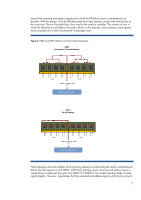
HP ProLiant G7 AMD 4-way architecture DDR3 DIMMs DDR3 DIMMs DDR3 DIMMs CPU CPU CPU HyperTransport Links The AMD-based ProLiant G7 servers use essentially the same processor/memory architecture for both 2P and 4P systems. Each processor has 4 memory controllers, each with a channel supporting - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 12
has not yet been fully characterized. Table 4. Theoretical maximum memory throughput for 4P ProLiant servers Intel-based 4P ProLiant G5 Intel-based 4P ProLiant G7 AMD-based 4P ProLiant G6 AMD-based 4P ProLiant G7 Theoretical maximum memory bandwidth 38.4 GB/s (FBDIMMs) 136.4 GB/s 51.2 GB/s 169 - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 13
ProLiant servers. Table 5. Memory latency of DDR2 and DDR3 in Intel-based ProLiant servers Unloaded latency Loaded latency 2P ProLiant G5 DDR2 at 667 MT/s 126 ns 2P ProLiant G6 DDR3 at 800 MT/s 80 ns 147 ns 140 ns 2P ProLiant G6 systems that are capable of supporting DDR3 at 1333 MT/s, - HP ProLiant DL380p | DDR3 memory technology - Page 14
Configuration Recommendations for HP ProLiant G6 Servers Memory technology evolution: an overview of system memory technologies HP ProLiant Server Memory web page Web address http://h20195.www2.hp.com/v2/GetPDF.aspx/c01750914.p df http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManu al/c00256987
DDR3 memory technology
Technology brief
Abstract
..............................................................................................................................................
2
DDR3 architecture
................................................................................................................................
2
Types of DDR3 DIMMs
.....................................................................................................................
2
DDR3 memory speeds
......................................................................................................................
2
Memory power consumption
.............................................................................................................
3
Low voltage DDR3 memory
...............................................................................................................
4
Core DDR3 Technologies
......................................................................................................................
4
Fly-by topology
................................................................................................................................
4
On-die Termination
..........................................................................................................................
6
Address parity checking on RDIMMs
..................................................................................................
6
DIMM Temperature sensor
................................................................................................................
6
DDR3 memory and NUMA systems architectures
.....................................................................................
7
Older server architectures
.................................................................................................................
7
DDR3 and the new systems architecture
..............................................................................................
8
DDR3 and Intel 4P architecture
..........................................................................................................
9
DDR3 and AMD 2P/4P systems architecture
.....................................................................................
10
Memory throughput with DDR3
...........................................................................................................
11
System memory bandwidth
..............................................................................................................
11
DDR3 latency
................................................................................................................................
12
Achieving best performance with DDR3 memory
...................................................................................
13
Maximizing system throughput
.........................................................................................................
13
Minimizing memory latency
............................................................................................................
13
Using balanced memory configurations
............................................................................................
13
Conclusion
........................................................................................................................................
14
For more information
..........................................................................................................................
14
Call to action
....................................................................................................................................
14