HP StorageWorks MSA 2/8 HP StorageWorks Extended Fabric V3.1.x/4.1.x User Guid - Page 19
Configuring an Extended Fabric Connection
 |
View all HP StorageWorks MSA 2/8 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
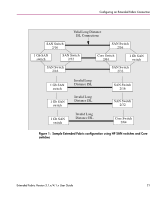
Configuring an Extended Fabric Connection 3 The Extended Fabric feature achieves long distance connections by allocating more frame buffers for Fibre Channel traffic. Long distance connections require more frame buffers than regular ISL connections. The greater the distance level of a ISL long distance connection, the more frame buffers are required. This affects the amount of buffers left over in the quad. A quad is defined as a group of four adjacent ports that share a common pool of frame buffers. In an HP StorageWorks SAN Switch (or port card in the Core Switch 2/64), ports 0 through 3 belong to a single quad, ports 4 through 7 belong to a single quad, and so on. Since the total number of frame buffers is limited in a quad when one port in a quad is configured as a long distance port, all remaining ports in the same quad must be configured appropriately. Refer to the "Long Distance Port Matrix" on page 27. Configuring long distance connections between core switches impacts available ISL ports because normal ISLs are required for connections from core switches to edge switches. When configuring long distance ISLs, make sure to balance the need between long distance ISL connections and core-to-edge ISL connections within a switch. Configuring long distance ISLs between core and edge switches is possible, but is not a recommended practice. Extended Fabric Version 3.1.x/4.1.x User Guide 19