TP-Link TD-W300KIT User Guide - Page 29
TL-WN821N, Wireless Mode, Wireless Mode when Starting an, Ad Hoc, Network, 11 Authentication Mode,
 |
View all TP-Link TD-W300KIT manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
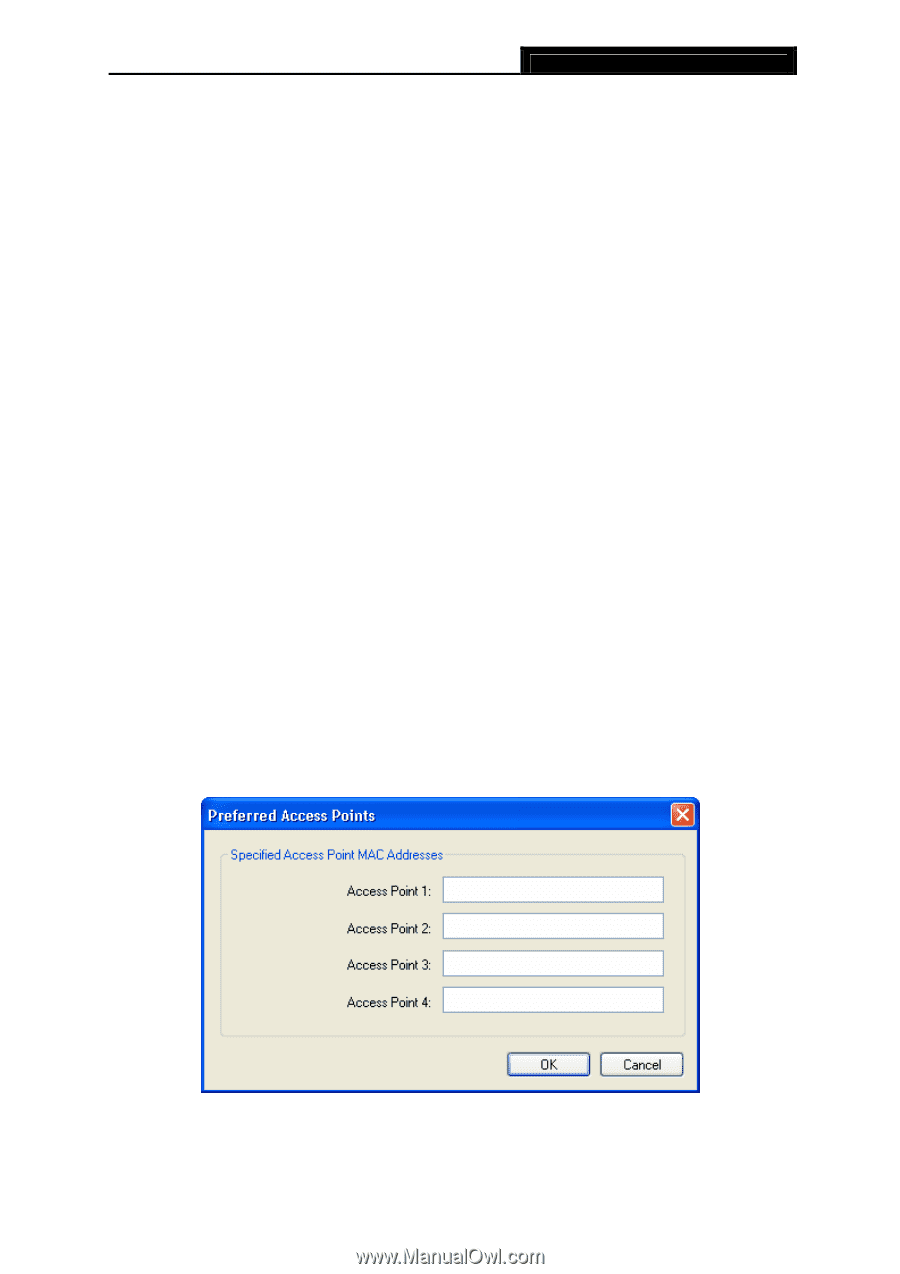
TL-WN821N 300Mbps Wireless N USB Adapter 2) An Ad-Hoc network contains only clients, such as laptops with wireless desktop adapters. All the adapters must be in Ad-Hoc mode to communicate. ¾ Wireless Mode: Specifies 2.4 GHz 150 Mbps, 2.4 GHz 54 Mbps or 2.4 GHz 11 Mbps operation in an access point network. The Wireless adapter must match the wireless mode of the access point with which it associates. ¾ Wireless Mode when Starting an Ad Hoc Network: Specifies 2.4 GHz 54/11 Mbps to start HH H an Ad Hoc network if no matching network name is found after scanning all available modes. This mode also allows the selection of the channel that the Wireless Adapter uses. The channels available depend on the regulatory domain. If the adapter finds no other ad hoc adapters, the channel that the adapter starts the ad hoc network with will be selected automatically. The Adapter must match the wireless mode and channel of the clients it associates. ¾ 802.11 Authentication Mode: Select which mode the Adapter uses to authenticate to an access point: • Auto - Automatic causes the adapter to attempt authentication using shared, but switches it to open authentication if shared fails. • Open - Open System enables an adapter to attempt authentication regardless of its WEP settings. It will only associate with the access point if the WEP keys on both the adapter and the access point match. • Shared - Shared-key only allows the adapter to associate with access points that have the same WEP key. For infrastructure (access point) networks, click Preferred APs... to specify four access points at most to the client adapter that attempts to be associated to the access points. The four access points have different priorities; the frontal has the higher priority. Figure 3-7 23