ZyXEL GS1500-24P User Guide - Page 79
Overview, What You Can - video
 |
View all ZyXEL GS1500-24P manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 79 highlights
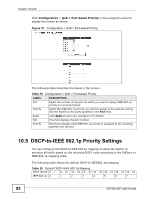
CHAPTER 10 QoS This chapter introduces the quality of service (QoS) parameters you can configure on the Switch. 10.1 Overview Quality of Service (QoS) refers to both a network's ability to deliver data with minimum delay, and the networking methods used to control the use of bandwidth. Without QoS, all traffic data is equally likely to be dropped when the network is congested. This can cause a reduction in network performance and make the network inadequate for time-critical application such as video-ondemand. It can be used to prioritize source-to-destination traffic flows. All packets in the flow are given the same priority. You can configure the Switch to prioritize traffic even if the incoming packets are not marked with IEEE 802.1p priority tags or change the existing priority tags based on the criteria you select. It also uses queuing algorithms to allow switches to maintain separate queues for packets from each individual source or flow and prevent a source from monopolizing the bandwidth. 10.2 What You Can Do Use the Port-based Priority screen (Section 10.4 on page 81) to assign a IEEE 802.1p priority to packets based on the ingress (incoming) port of the packet. Use the DSCP-based Priority screen (Section 10.5 on page 82) to assign priority to packets based on their Differentiated Services Code Points (DSCPs). Use the Policy-based Priority screens (Section 10.6 on page 83) to classify and prioritize certain traffic flows. GS1500-24P User's Guide 79