Acer Veriton M661 Intel Matrix Storage and RAID - Page 8
Raid1, Raid5, Raid10
 |
View all Acer Veriton M661 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
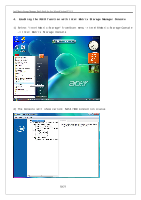
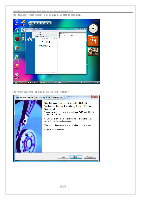
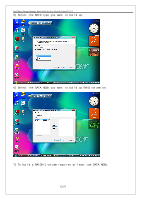
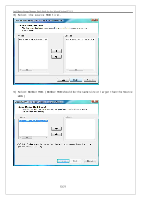
Intel Matrix Storage Manager Quick Guide for Acer Selected Veriton PC V1.1 multiple controllers with RAID1 only one drive per controller ¾ Very simple design ¾ Easy to implement ¾ Twice the Read transaction ¾ rate of single disks, same Write transaction rate as single disks ¾ ¾ 100 percent redundancy of data means no rebuild is necessary in case of a disk failure, just a copy to the replacement disk ¾ Transfer rate per block is equal to that of a single disk ¾ Under certain circumstances, RAID1 can sustain multiple simultaneous drive failures ¾ Simplest RAID storage subsystem design RAID5 ¾ Highest Read data transaction ¾ rate ¾ Medium Write data transaction ¾ rate ¾ Low ratio of ECC (parity) disks to data disks means high ¾ RAID10 efficiency ¾ Good aggregate transfer rate ¾ Very high I/O rates are ¾ achieved by striping RAID1 segments ¾ ¾ Excellent solution for sites that would normally use RAID1 Highest disk overhead of all RAID types (100%) - inefficient May not support hot-swap of failed disk when implemented using software RAID Most complex controller design Difficult to rebuild in the event of a disk failure (as compared to RAID 1) Individual block data transfer rate same as single disk Very limited scalability at a very high inherent cost Expensive to maintain 8/21