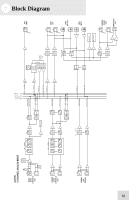
Alesis MultiMix 6 FX Reference Manual - Page 35
Glossary
 |
View all Alesis MultiMix 6 FX manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 35 highlights
Glossary Here are the definitions to some terms you'll probably encounter while using your MultiMix-6FX. Term aux (auxiliary) balance bus channel channel strip clipping condenser microphone dB (decibel) detent dry dynamic microphone effects processor EQ (equalizer) Definition An additional set of outputs and inputs found on many mixers. These allow the addition of external effects and other audio sources. A control that lets you control the position of sound in a stereo signal by altering the relative levels of the left and right channels. The electrical component that carries signals from multiple sources to a single destination such as an amplifier. A path through which an audio signal flows. A section of a mixer on which reside controls like a fader, EQ and pan for manipulating the signal of an input channel. The cutting of an audio signal caused by a level that is too great for a mixer circuit to handle. A type of high-quality microphone that produces a weak signal, usually requiring an external power source like the ones provided by your MultiMix-6FX's XLR mic inputs. A common unit of measure for audio. A point of resistance in the path that a mixer knob or fader travels. Detents are used to mark important settings. As you turn the knob or slide the fader, you'll feel it "click" into the detent. Term used to describe an audio signal free of effects. The opposite of "wet." A common type of microphone that does not require external power. Dynamic microphones are generally cheaper than condenser microphones. A unit whose purpose is to provide effects for audio signals. Some common effects include reverb, chorus, flange and delay. Effects processors come in many shapes and sizes, from small pedals up to rectangular rackmount units. The part of your mixer (or other device) that manipulates an audio signal by lowering the level of some frequencies and increasing the levels of others. EQ is used to fine-tune a signal's highs and lows. 33