Biostar K8NHA GRAND K8NHA Grand user's manual - Page 19
Features and Benefits
 |
View all Biostar K8NHA GRAND manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
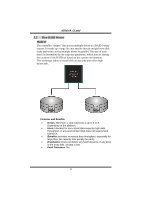
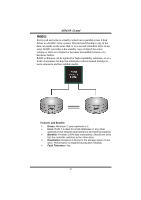
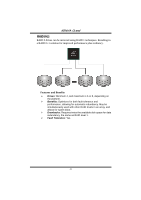
K8NHA Grand 5.3 HOW RAID WORKS RAID 0: The controller "stripes" data across multiple drives in a RAID 0 array system. It breaks up a large file into smaller blocks and performs disk reads and writes across multiple drives in parallel. The size of each block is determined by the strip size parameter, which you set during the creation of the RAID set based on the system environment. This technique reduces overall disk access time and offers high bandwidth. Features and Benefits Drives: Minimum 1, and maximum is up to 6 or 8. Depending on the platform. Uses: Intended for non-critical data requiring high data throughput, or any environment that does not require fault tolerance. Benefits: provides increased data throughput, especially for large files. No capacity loss penalty for parity. Drawbacks: Does not deliver any fault tolerance. If any drive in the array fails, all data is lost. Fault Tolerance: No. 19