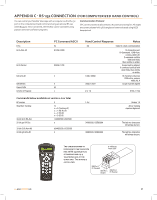
Celestron CPC Deluxe 925 HD Computerized Telescope CPC Deluxe HD Manual - Page 38
by Bernhard Voldemar Schmidt
 |
View all Celestron CPC Deluxe 925 HD Computerized Telescope manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
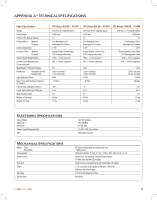
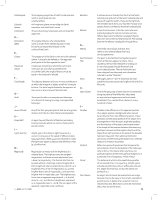
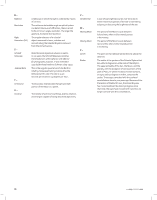
R - Reflector Resolution Right Ascension: (RA) S - Schmidt Telescope Sidereal Rate T - Terminator U - Universe A telescope in which the light is collected by means of a mirror. The minimum detectable angle an optical system can detect. Because of diffraction, there is a limit to the minimum angle, resolution. The larger the aperture, the better the resolution. The angular distance of a celestial object measured in hours, minutes and seconds along the Celestial Equator eastward from the Vernal Equinox. Rated the most important advance in optics. in 200 years, the Schmidt telescope combines the best features of the refractor and reflector for photographic purposes. It was invented in 1930 by Bernhard Voldemar Schmidt (1879-1935). This is the angular speed at which the Earth is rotating. Telescope tracking motors drive the telescope at this rate. The rate is 15 arc seconds per second or 15 degrees per hour. The boundary line between the light and dark portion of the Moon or a planet. The totality of astronomical things, events, relations and energies capable of being described objectively. V - Variable Star W - Waning Moon Waxing Moon Z - Zenith Zodiac A star whose brightness varies over time due to either inherent properties of the star or something eclipsing or obscuring the brightness of the star. The period of the Moon's cycle between full and new, when its illuminated portion is decreasing. The period of the Moon's cycle between new and full, when its illuminated portion is increasing. The point on the Celestial Sphere directly above the observer. The zodiac is the portion of the Celestial Sphere that lies within 8 degrees on either side of the Ecliptic. The apparent paths of the Sun, the Moon, and the planets, with the exception of some portions of the path of Pluto, lie within this band. Twelve divisions, or signs, each 30 degrees in width, comprise the zodiac. These signs coincided with the zodiacal constellations about 2,000 years ago. Because of the Precession of the Earth's axis, the Vernal Equinox has moved westward by about 30 degrees since that time; the signs have moved with it and thus no longer coincide with the constellations. 36 >> www.celestron.com