Compaq 307560-001 Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability
Compaq 307560-001 - ProLiant - 2500R Manual
 |
UPC - 743172470379
View all Compaq 307560-001 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Compaq 307560-001 manual content summary:
- Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 1
WHITE PAPER [September 1997] Prepared By Microsoft Windows NT Integration Team Compaq Computer Corporation CONTENTS Disk Subsystem Overview 3 Disk-Related Performance Characteristics 4 Like Drive Scalability 17 Like Capacity Scalability 19 Disk Controller Scalability 24 Performance Measurement - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 2
, MultiLock, QuickBlank, QuickLock, UltraView, Innovate logo, Wonder Tools logo in black/white and color, and Compaq PC Card Solution logo are trademarks and/or service marks of Compaq Computer Corporation. Other product names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 3
can help you understand how latency, average seek time, transfer rates and file system or disk controller caching can affect your disk subsystem performance. Once we Lab of hardware and software products from Compaq and other vendors. The test environment that Compaq selected might not be the same as - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 4
Subsystem Testing Environment Environment Equipment Used Server Software Configuration Microsoft Windows NT Server version 4.0 Service Pack 2 Compaq Support Software Diskette 1.20A Client Configuration Compaq Deskpro 575 Netelligent 10/100 TX PCI UTP Controller and MS-DOS NetBench 5.0 Test - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 5
ECG025.0997 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... Table 2: (cont.) Disk Performance Measurement Terms Terms Description Latency The time required for the disk to spin one complete revolution. Average Latency The time required for the disk to spin half a revolution. Average Access Time The average length - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 6
ECG025.0997 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... One method to decrease seek time is to distribute data across multiple drives. For instance, the initial configuration in Figure 1 shows a single disk containing data. The new configuration reflects the data being striped across multiple disks. This method - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 7
ECG025.0997 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... Average Latency Manufacturers have built and continue to build hard disks that spin at designated rates. In the early years of the personal computer (PC) industry, hard disks on the market could spin at approximately 3600 RPMs. As the market demand for better - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 8
WHITE PAPER (cont.) Note: Remember that the disks used in Figure 2 are identical in size and RAID configuration. ECG025.0997 ... However, be aware that the average latency time might not always decrease when adding more drives to your system. For example, in Figure 2 - Example 2, the new - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 9
transferring data to and from the disk(s) to a computer. The main parts of a disk subsystem are as follows: • Hard Disks • SCSI Channel • Disk Controller • I/O Bus • File System and Disk Controller Caching 9 - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 10
WHITE PAPER (cont.) Remember that the slowest disk subsystem component determines the overall throughput of the system. ECG025.0997 ... In order to share information, all of the disk subsystem components have to communicate with each other, as shown in Figure 4. The disk subsystem components - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 11
a special interface used to communicate with the SCSI bus. This interface, defined in disk drive characteristic specification documents, identifies the type of controller the drive supports not the transfer rate of the disk. For example, if you are using a Wide-Ultra drive you know that this drive - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 12
greater than the SCSI channel. Disk Controller Transfer Rates Disk controllers are continuously being upgraded to support wider data paths and faster transfer rates. Currently, Compaq supports three industry standard SCSI interfaces on their disk controllers, as shown in Table 5. Controller Name - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 13
I/O bus architecture specification that supports 8- and 16-bit data throughput paths. Supports bus-mastering on 16-bit file system cache being the first) likely of all of the disk subsystem components to be a performance bottleneck. To illustrate the point, it would take a minimum of three Compaq - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 14
system first tries to complete the READ request by retrieving the data from the file system cache (memory). If it is not there, the system has to retrieve checks to see if the requested data is in memory (i.e., File system cache). Operating system passes the requested information to the application - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 15
... Table 7 lists the Host bus transfer rates for the following Compaq servers: Table 7: Host Bus (Memory) Transfer Rates Server Name system by taking advantage of posted writes. Posted writes take place when file system or disk controller caching temporarily holds one or more blocks of data - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 16
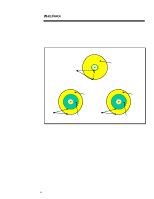
ECG025.0997 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... Concurrency Concurrency is the process of eliminating the wait time involved to retrieve and return requested data. It takes place when multiple slow devices (e.g., disk drives) place I/O requests on a single faster device (e.g., SCSI bus). As shown in Figure 6, - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 17
ECG025.0997 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... Concurrency is very effective in a multi-drive environment because, while one drive is retrieving data, another request can be coming across the SCSI bus as shown in Figure 7. When using multiple drives, each drive can send data across the SCSI bus as soon as it - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 18
available for future disk controllers that might be necessary to support future capacity requirements. Like Drive Scaling Like drive scaling more drives out weigh the performance gain?". To answer this question, Compaq tested controllers using the same RAID configuration and added drives, then - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 19
because you have more drives processing disk requests. Using smaller size drives limits your maximum capacity per controller. For example, the Compaq SMART-2 Array Controller supports up to 14 drives. By using fourteen 2GB drives, your data capacity equals 28GB. By using fourteen 4GB drives, your - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 20
the performance would be because more I/O requests are being concurrently processed. Overall our single disk controller like capacity tests provide evidence that support our theory on concurrency. For example, if you need 8 Gigabytes of storage capacity, our test show the benefits of using four 2GB - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 21
ECG025.0997 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... In Figure 10, our tests show that if you require 24 Gigabytes of storage capacity the performance gain of 33% is in using twelve 2GB disks instead of six 4GB disks. With concurrency taking place by using multiple lower capacity drives (twelve 2GB drives), more - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 22
ECG025.0997 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... Like Capacity Scaling (RAID 5 - 1 Controller) 14,000,000 12,000,000 10,000,000 7+1 x 2GB 3+1 x 4GB Server Throughput (Bytes/sec) 8,000,000 6,000,000 54% 4,000,000 2,000,000 0 4 8 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 52 56 57 Number of Clients Figure 11: Like - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 23
of drives, improves the performance (more concurrency). Using smaller size drives limits your maximum capacity per controller. For example, the Compaq SMART-2 Array Controller supports up to 14 drives. By using fourteen 2GB drives, your data capacity equals 28GB. By using fourteen 4GB drives, your - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 24
ECG025.0997 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... Summary of Findings - Like Capacity Scaling Our test results conclude that by doubling the number of drives in a system, regardless of the data storage capacity requirements and the fault tolerance used, we consistently received an improvement in performance. - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 25
WHITE PAPER (cont.) Note: Within each test comparison, the total disk capacity remained constant. ECG025.0997 ... Multiple Disk Controller Test Results In our multiple disk controller tests we found that concurrency coupled with adding disk controllers to an environment increases system - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 26
ECG025.0997 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... Disk Controller Scaling (RAID 0) Server Throughput (Bytes/sec) 20,000,000 18,000,000 16,000,000 14,000,000 12,000,000 10,000,000 8,000,000 6,000,000 4,000,000 2,000,000 0 4 12 x 4GB, 1 Ctr 3% 12 x 4GB, 2 Ctr 8 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 52 56 57 Number of - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 27
in identifying and managing performance issues while using Windows NT on Compaq server hardware. These tools are now available on the Compaq Resource Paq for Microsoft Windows NT. To obtain a copy of the Compaq Resource Paq, go to the Compaq Microsoft Frontline Partnership page located on the web at - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 28
and Power Supply. These counters require Compaq Support Software Version 1.21a or later for Microsoft Windows NT and Compaq Insight Manager 3.30 or later. it can help you protect your data. Use Table 13, as a guide in deciding which method is right for your network environment. Fault Tolerance This - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 29
gathered these concepts and summarized the information. These concepts are: • Disk-Related Measurement Terms • Understanding the Transfer Rates within the Disk Subsystem • The Importance of File System Cache • Benefits of Scaling 29 - Compaq 307560-001 | Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 30
disk subsystem generally determines the overall throughput of the system. The Importance of File System Cache Improving performance on a disk subsystem comes with understanding the impact of file system caching. File system cache is the single fastest component within the disk subsystem; therefore

W
HITE
P
APER
Help us improve our technical communication.
Let us know what you think about the
technical information in this document.
Your feedback is valuable and will help us structure
future communications.
Please send your comments to:
1
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
ECG025.0997
[September 1997]
Prepared By
Microsoft Windows NT
Integration Team
Compaq Computer
Corporation
C
ONTENTS
Disk Subsystem
Overview
.....................
3
Disk-Related
Performance
Characteristics
............
4
Like Drive
Scalability
.................
17
Like Capacity
Scalability
.................
19
Disk Controller
Scalability
.................
24
Performance
Measurement Tools... 27
Preventing Data
Loss while
Maintaining
Performance
..............
28
Disk Subsystem
Summary of
Findings
....................
29
Disk Subsystem Performance and
Scalability
In today's networking environments, the disk subsystem is a key element in determining
overall system performance.
The goal of this paper is to provide informative test results
and performance-related information for various disk subsystems, to assist systems
engineers and network administrators in making decisions on disk subsystem installation,
optimization, and configuration.
This white paper also provides information on using Fault Tolerance to prevent data loss,
while maintaining system performance.
Finally, this paper provides a section discussing
the advantages and disadvantages of RAID technology.