Compaq 307560-001 Disk Subsystem Performance and Scalability - Page 16
Concurrency
 |
UPC - 743172470379
View all Compaq 307560-001 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 16 highlights
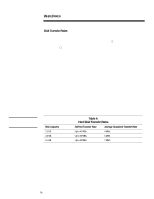
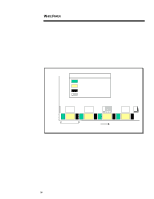
ECG025.0997 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... Concurrency Concurrency is the process of eliminating the wait time involved to retrieve and return requested data. It takes place when multiple slow devices (e.g., disk drives) place I/O requests on a single faster device (e.g., SCSI bus). As shown in Figure 6, a request for data comes across the SCSI Bus asking the disk drive to retrieve some information. The disk drive retrieves then sends the requested data back to the server via the SCSI bus. The time it takes to complete this process seems to be acceptable at first glance until you examine the amount of time the SCSI bus remains idle. This idle time shown in Figure 6 is the amount of time the SCSI bus is waiting for the disk drive to complete the request. This valuable time could be used more efficiently in an environment taking advantage of concurrency. Legend Request for Data (SCSI Bus) Retrieving Data (Disk Drive) Sending Data (SCSI Bus) Idle Time (SCSI Bus) SCSI Bus Idle Drive 1 1 1 12 First I/O Request 2 23 Time 3 34 4 4 Figure 6: I/O request timing diagram for a single drive configuration. 16