D-Link DGS-3208TG User Guide - Page 30
Port Trunking, Table 5-1., User-selective STA parameters, Port trunking example
 |
UPC - 790069239366
View all D-Link DGS-3208TG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
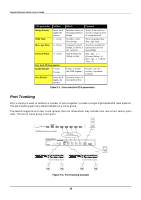
Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Guide STA parameters Settings Effects Comment Bridge Priority lower the #, Increases chance of Avoid, if the switch is higher the becoming the Root used in workgroup level priority Bridge of a large network Hello Time 1 - 10 sec. No effect, if not Root Bridge Never set greater than Max. Age Time Max. Age Time 6 - 40 sec. Compete for Root Avoid low number for Bridge, if BPDU is unnecessary reset of not received Root Bridge Forward Delay 4 - 30 sec. High # delays the change in state Max. Age ≤ 2 x (Forward Delay - 1) Max. Age ≥ 2 x (Hello Time + 1) Port-level STA parameters Enable/Disable Enable/ Disable Enable or disable this LAN segment Disable a port for security or problem isolation Port Priority lower the #, Increases chance of higher the become Root Port priority Table 5-1. User-selective STA parameters Port Trunking Port trunking is used to combine a number of ports together to make a single high-bandwidth data pipeline. The participating parts are called members of a trunk group. The Switch supports up to four trunk groups, the first three which may include from two to four switch ports each. The fourth trunk group is two ports. Figure 5-3. Port trunking example 18