D-Link DGS-3208TG User Guide - Page 55
Con MAC Address Filtering
 |
UPC - 790069239366
View all D-Link DGS-3208TG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 55 highlights
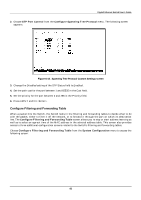
Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Guide Figure 6-20. Static Forwarding Table screen By mapping a port to a destination MAC address, the Switch can permanently forward traffic to the specified device, even after long periods of network inactivity or during times of network congestion. To make a change to the Static Forwarding Table screen, choose either Add or Remove in the Action field. Then enter the MAC Address, the Port number that permanently forwards traffic from the specified device, regardless of the device's network activity or current network congestion, enter a VLAN (if applicable), and press APPLY. The following fields at the top of the screen can be set: ♦ Action Choose Add or Remove for each entry from the table. ♦ MAC Address Enter a MAC address in this field at the top of the screen. This is the MAC address of the device that you are creating a permanent forwarding address for. A total of ten destination addresses per page will be seen at the bottom of the screen. The Switch can hold up to 256 entries. ♦ Port The port number is entered in this field at the top of the screen. The Switch will always forward traffic to the specified device through this port. The bottom of the screen will display a corresponding destination address. ♦ VLAN Enter the desired VLAN ID number. In the lower part of the screen, Destination MAC Address, Destination Port, VLAN, and Status are all read-only fields. The status of the static forwarding table entry can be "in use" or "not apply." "Not apply" means that there is a static filter for the same MAC address. Static filters always take precedence over static forwarding entries. The Switch will automatically upgrade the Status to "in use" once the static filter is removed. Configure MAC Address Filtering The Static Filtering Table screen contains filtering information configured into the Switch by (local or network) management specifying the set of ports to which packets received from specific ports and containing specific destination addresses are not allowed to be forwarded. You can use the Static Filtering Table screen for network security purposes thereby discarding unwanted addresses from the Forwarding Table. Dynamic Filtering and Static Filtering are among the two important features of the Static Filtering Table. They are defined here briefly as follows. Dynamic Filtering is when a dynamic entry is created by the Learning Process as a result of observation of network traffic in the Filtering Database. Static Filtering is 43