Dell PowerConnect 2808 User's Guide - Page 125
Interface, Designated, Alternate, Backup, Disabled, Classic STP, Rapid STP, Multiple STP
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect 2808 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 125 highlights
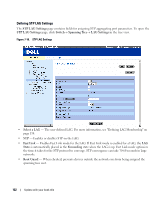
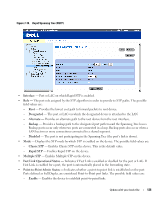
Figure 7-19. Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) • Interface - Port or LAG on which Rapid STP is enabled. • Role - The port role assigned by the STP algorithm in order to provide to STP paths. The possible field values are: - Root - Provides the lowest cost path to forward packets to root device. - Designated - The port or LAG via which the designated device is attached to the LAN. - Alternate - Provides an alternate path to the root device from the root interface. - Backup - Provides a backup path to the designated port path toward the Spanning Tree leaves. Backup ports occur only when two ports are connected in a loop. Backup ports also occur when a LAN has two or more connections connected to a shared segment. - Disabled - The port is not participating in the Spanning Tree (the port's link is down). • Mode - Displays the STP mode by which STP is enabled on the device. The possible field values are: - Classic STP - Enables Classic STP on the device. This is the default value. - Rapid STP - Enables Rapid STP on the device. • Multiple STP - Enables Multiple STP on the device. • Fast Link Operational Status - Indicates if Fast Link is enabled or disabled for the port or LAG. If Fast Link is enabled for a port, the port is automatically placed in the forwarding state. • Point-to-Point Admin Status - Indicates whether a point-to-point link is established on the port. Ports defined as Full Duplex are considered Point-to-Point port links. The possible field values are: - Enable - Enables the device to establish point-to-point links. Update with your book title 125