Dell PowerVault MD3000i Dell PowerVault MD3000/MD3000i Array Tuning Best Pract - Page 13
Dell™ PowerVault MD3000 and MD3000i Array Tuning Best Practices, Setting the Storage Array Cache
 |
View all Dell PowerVault MD3000i manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
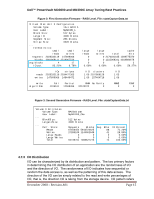
Dell™ PowerVault MD3000 and MD3000i Array Tuning Best Practices 4.6.3 Setting the Storage Array Cache Block Size Configured through the CLI - This command is available at the storage array level and effects all virtual disks and disk-groups. Cache Block Size - Cache Block Size refers to the way cache memory is segmented during allocation and affects all virtual disks in an array. On the MD3000 and MD3000i, settings of 4KiB and 16KiB are available with 4KiB being the default. A dramatic impact on performance can occur by choosing the correct cache block size setting specific to the system's I/O profile. If the typical I/O size is ≥16KiB, which is typical with sequential I/O, set the storage array Cache Block Size to 16. For smaller (≤8KiB) I/O, especially in highly random or transactional use cases, the default 4KiB setting is preferred. As this setting affects all virtual disks on a storage array, changing it should be done with attention to the I/O needs of the application. Option Drive Type RAID Level Segment Size 1 Write cache with mirroring Read-ahead cache Cache Block Size 1 Table 2: Storage Array Standard Configuration Specifications MDSM GUI configuration templates File System Database Multimedia Selectable Selectable Selectable Selectable Selectable Selectable 128KiB 128KiB 256KiB CLI Options Selectable 0, 1/10, 5, 6 8KiB, 16KiB, 32KiB, 64KiB, 128KiB, 256KiB, 512KiB Fixed to on Fixed to on Fixed to on On or Off On Off On On or Off Array Defaults to 4KiB 4KiB, 16KiB 1 The MDSM CLI Guide and SMcli application may use the legacy terminology of KB to mean Kilobytes, or 210 bytes. Throughout this whitepaper, the SI term kibibytes are used instead. When formulating an SMcli command the KB postfix is however still required. IEEE 1541-2002 and IEC 60027-2 standards detail units of measurement prefixes for binary multiples. December 2008 - Revision A01 Page 13