Dell PowerVault MD3000i Dell PowerVault MD3000/MD3000i Array Tuning Best Pract - Page 19
Dell™ PowerVault MD3000 and MD3000i Array Tuning Best Practices, 7.5 Write Algorithm Data
 |
View all Dell PowerVault MD3000i manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
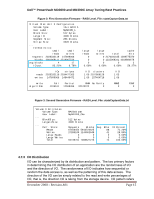
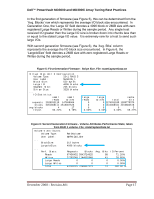
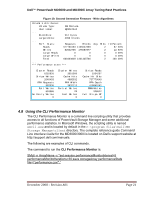
Dell™ PowerVault MD3000 and MD3000i Array Tuning Best Practices Figure 8: Second Generation Firmware- Stripe distribution. File: stateCaptureData.txt Volume 0 Attributes: Volume Type: RAIDVolume User Label: MyRAID10_One ... BlockSize: 512 bytes 3. LargeIoSize: 4096 blocks ... Perf. Stats: Requests Blocks Reads 67456452 5943724625 Writes 27283249 1144902648 Large Reads 0 0 1. Large Writes 0 0 Total 94739701 7088627273 ... *** Performance stats *** Avg. Blks 88 41 0 0 74 IO Percent 71.20% 28.80% 0.00% 0.00% 100.33% Cluster Reads Cluster Writes Stripe Reads 6252626 3015009 5334257 Stripe Writes Cache Hits Cache Hit Blks 2040493 4685032 737770040 2. RPA Requests RPA Width RPA Depth 982036 3932113 418860162 Full Writes Partial Writes 2. 653386 29 RMW Writes 328612 No Parity Writes Fast Writes Full Stripe WT 0 0 0 4.7.5 Write Algorithm Data It is important to understand the effect determining the most suitable RAID level can be a daunting task. Understanding the effect of which write algorithm is in use is an important part of RAID Level balance. The possible choices in first generation firmware, as seen in Figure 9, are Full, Partial, RMW, RMW2, and the Full Stripe Write-Through. RMW2 was folded into RMW statistics in the second generation firmware (see Figure 10). The Full algorithm takes an entire stripe of data and dumps it to the disk, depending on the RAID level of choice, P or P and Q will get calculated at this point. This is the most efficient type of write that can be performed, and the design of a disk group should be around maximizing full writes. Partial writes are when less than a full stripe of data non-aligned with segment boundaries are modified and written. In RAID level 5 and 6 this is more complex, as parity data must be recalculated for the whole stripe. Partial writes are a worst-case algorithm and should be minimized. Larger quantities of partial writes than full writes can indicate use of an inappropriate segment size. December 2008 - Revision A01 Page 19